Hair Transplantation is a surgical procedure that aims to restore hair growth in areas of the scalp with limited or no hair. There are two main techniques used in hair transplantation: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). The choice between FUT and FUE depends on various factors, including the patient’s hair type, the size of the area to be treated, and the patient’s personal preference.
Hair Transplant Methods
What is a FUE hair transplant?
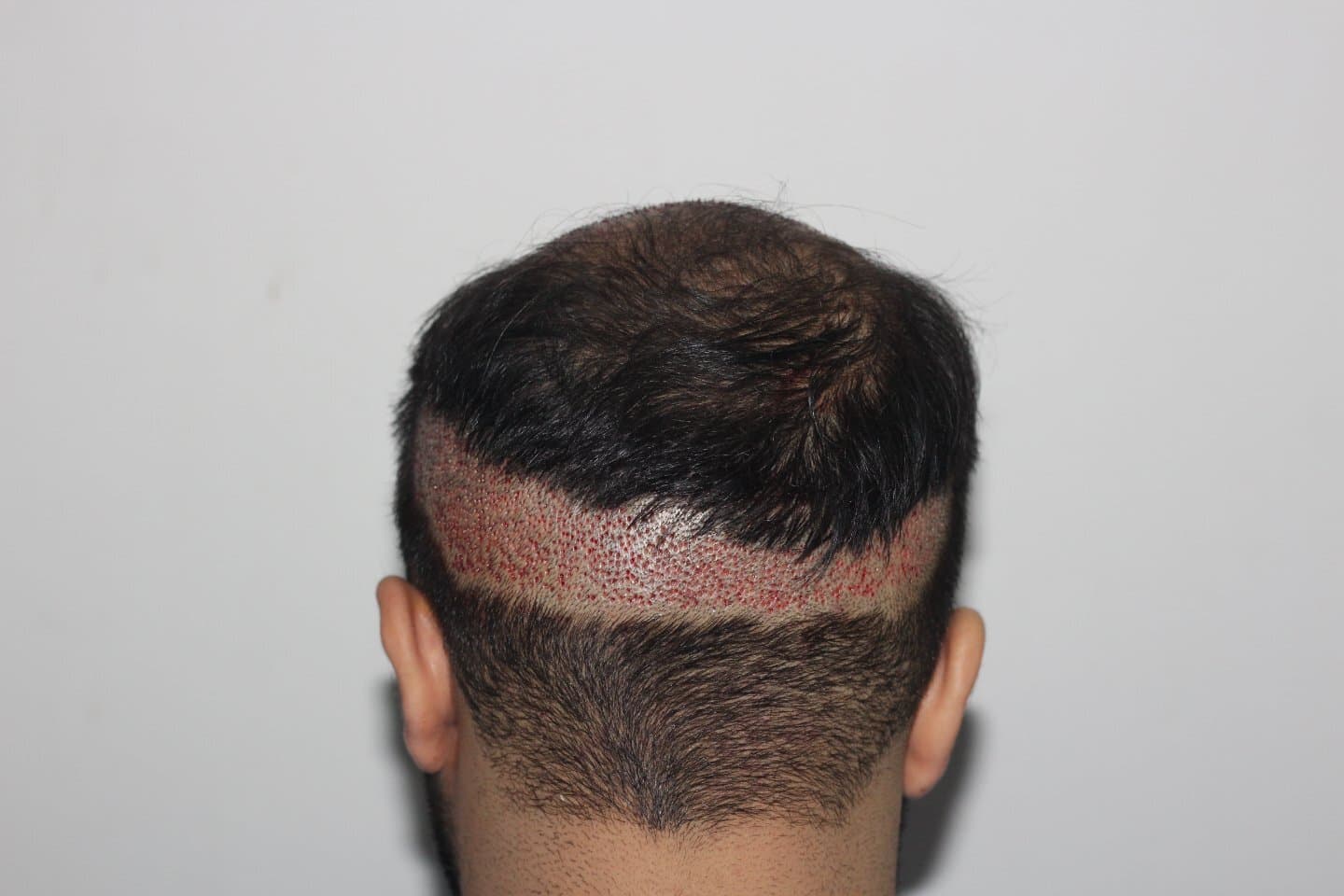
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is a modern and advanced technique used in hair transplantation. Unlike traditional methods, FUE offers a less invasive approach to hair restoration, resulting in minimal scarring and a more natural-looking outcome.
The FUE procedure begins with the surgeon shaving or trimming the hair at the donor site, typically the back or sides of the head where hair growth is still abundant. The surgeon then uses a specialized tool to extract individual hair follicles from this area. Each follicle contains 1-4 hairs, which are the building blocks for hair growth.
Once the follicles are extracted, they are carefully prepared for transplantation. This involves inspecting the follicles under a microscope and selecting the healthiest ones for implantation. The preparation process is crucial to ensure the highest survival rate of the transplanted follicles and to achieve the best possible aesthetic result.
The next step is the creation of recipient sites in the balding or thinning areas of the scalp. The surgeon makes tiny incisions in these areas, taking into account the direction, angle, and density of the natural hair growth. This meticulous process is essential to ensure that the transplanted hair will blend seamlessly with the existing hair and grow in a natural-looking pattern.
The final step is the implantation of the hair follicles into the recipient sites. The surgeon carefully inserts each follicle into the incisions, ensuring that they are placed at the correct depth and angle. This process requires a high level of skill and precision to achieve a natural and undetectable result.
What is a FUT hair transplant?
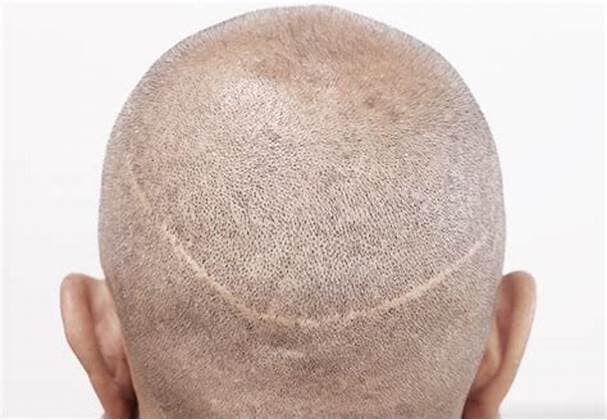
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), also known as the strip method, is a traditional technique used in hair transplantation. Despite being somewhat more invasive than newer methods like FUE, FUT can be a highly effective solution for hair restoration, particularly for individuals with extensive hair loss.
The FUT procedure begins with the surgeon removing a strip of skin from the donor area, usually the back or sides of the head where hair growth is still abundant. This strip contains numerous hair follicles, which are then dissected under a microscope into individual follicular units, each containing 1-4 hairs.
Once the follicular units are prepared, the surgeon creates recipient sites in the balding or thinning areas of the scalp. These are tiny incisions made in a pattern and direction that mimic natural hair growth. The prepared follicular units are then inserted into these recipient sites.
One of the key advantages of FUT is the ability to transplant a large number of grafts in a single session. This makes FUT a potentially more efficient choice for individuals with significant hair loss. Furthermore, because the follicles are removed in a strip and dissected under a microscope, there is less risk of follicle damage, which can result in a higher survival rate of the transplanted hair.
The Difference Between FUE and FUT
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) are the two primary techniques used in hair transplantation. While both methods aim to achieve the same goal of restoring hair growth, they differ significantly in their procedures, recovery times, and outcomes.
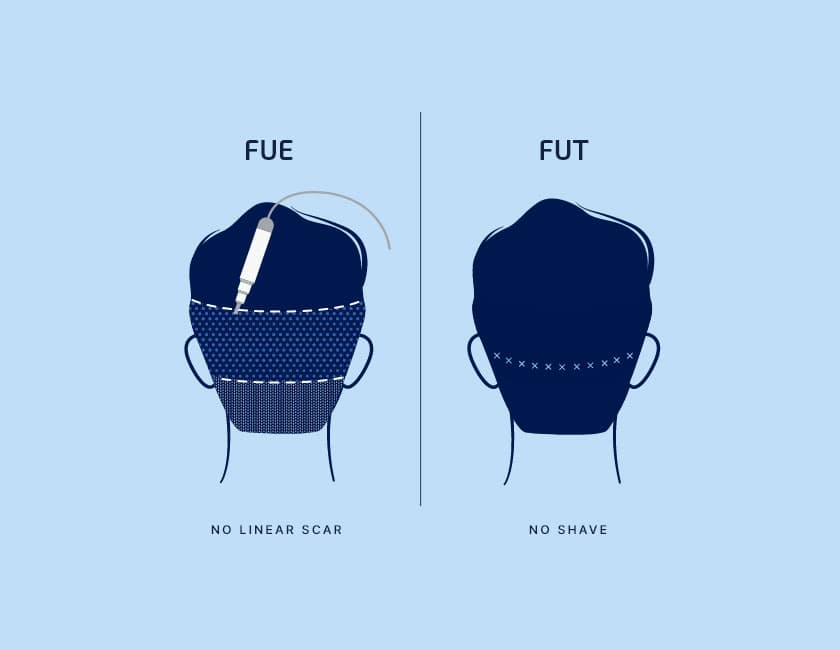
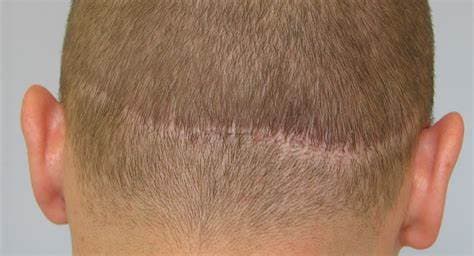
Procedure: The main difference between FUE and FUT lies in the way hair follicles are extracted from the donor area. In FUE, individual follicles are removed directly from the scalp using a specialized tool, leaving only small, dot-like scars. In contrast, FUT involves removing a strip of skin from the donor area, from which the follicles are then dissected. This method leaves a linear scar.
Scarring: FUE is often preferred for those who wish to wear their hair short, as the scarring is minimal and hard to detect. The linear scar left by FUT, on the other hand, can be more noticeable with short haircuts, but is typically concealed by longer hairstyles.
Number of Grafts: FUT can often allow for the transplantation of a larger number of grafts in a single session, making it a potentially more efficient choice for individuals with extensive hair loss. FUE, while less invasive, can be more time-consuming and may require multiple sessions to achieve similar coverage.
Recovery Time: The recovery time for FUE is generally shorter than that for FUT. Patients undergoing FUE can typically return to their normal activities within a few days, while those who choose FUT may require a few weeks to fully recover.
Aesthetics: Both FUE and FUT can produce natural-looking results when performed by an experienced surgeon. However, the success of the procedure and the aesthetics of the outcome can depend on various factors, including the skill of the surgeon, the quality and density of the donor hair, and the extent of hair loss.
Cost: FUE procedures are generally more expensive than FUT due to the more labor-intensive nature of the follicle extraction process.
FUE vs. FUT: Which one is right for me?
Choosing between Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) for hair transplantation is a decision that should be made based on your individual needs, lifestyle, and expectations. Here are some factors to consider:
Extent of Hair Loss: If you have extensive hair loss, FUT might be a better option as it allows for the transplantation of a larger number of grafts in a single session. However, if your hair loss is less severe, FUE could be sufficient.
Recovery Time: FUE generally has a quicker recovery time compared to FUT. If you need to return to work or your daily activities shortly after the procedure, FUE might be more suitable.
Scarring: If you prefer to wear your hair short, FUE might be a better choice as it leaves minimal and less noticeable scarring compared to the linear scar left by FUT.
Cost: Generally, FUE is more expensive than FUT due to the more labor-intensive nature of the follicle extraction process. If cost is a significant factor for you, this might influence your decision.
Personal Preference: Some people might prefer a less invasive procedure, even if it means more sessions or a higher cost, making FUE a more attractive option. Others might prioritize efficiency and choose FUT to get more grafts transplanted in a single session.
Medical Advice: It’s crucial to consult with a hair restoration specialist who can assess your hair loss pattern, donor hair quality, and overall health. They can provide personalized advice and help you understand the potential risks and benefits of each procedure.
In conclusion, the choice between FUE and FUT depends on the individual’s specific needs, preferences, and circumstances. It’s important to have a thorough consultation with a hair restoration specialist who can provide personalized advice based on an assessment of the individual’s hair loss pattern, donor hair quality, lifestyle, and budget. As with any medical procedure, it’s crucial to understand the potential risks and benefits before making a decision.
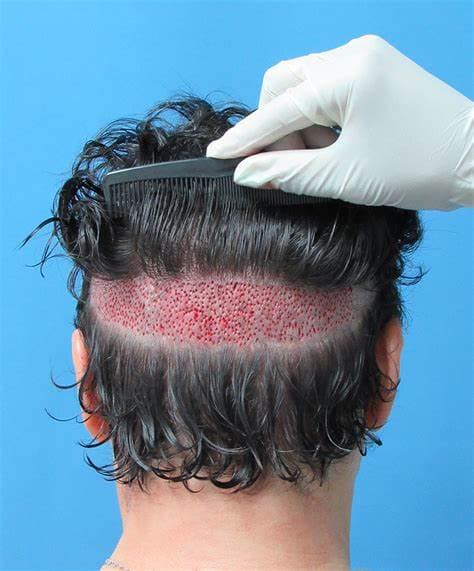
FUE Pros & Cons
Pros of FUE
Minimally Invasive: One of the main benefits of FUE is that it’s minimally invasive compared to other hair transplant methods. The procedure involves extracting individual hair follicles from the donor area, which results in less trauma to the scalp and a quicker recovery time.
Minimal Scarring: FUE leaves tiny, dot-like scars that are typically undetectable even under short hair. This is a significant advantage for those who wish to wear their hair short or shaved, as the scars from the procedure are virtually invisible.
Natural-Looking Results: Because FUE allows for the transplantation of individual follicular units, it can provide very natural-looking results. The surgeon can place the grafts in a pattern and direction that mimic natural hair growth, resulting in a seamless blend with the existing hair.
No Linear Scar: Unlike FUT, which leaves a linear scar on the back of the head, FUE does not. This can be a deciding factor for many patients who are concerned about the visibility of scarring.
Less Post-Operative Discomfort: Patients often report less discomfort during the recovery period with FUE compared to other methods. This is likely due to the fact that FUE does not involve the removal of a strip of tissue from the scalp.
Flexibility in Donor Areas: While the back of the head is the most common donor area, FUE allows for the extraction of hair from other parts of the body, such as the beard or chest. This can be beneficial for patients who do not have sufficient hair density at the back of the scalp.
Suitable for Early-Stage Hair Loss: FUE can be an excellent option for individuals who are in the early stages of hair loss, as it allows for targeted treatment of specific areas.
Cons of FUE
Time-Consuming: One of the main disadvantages of FUE is that it can be a time-consuming procedure. Because each follicle is extracted individually, the process can take several hours or even require multiple sessions, especially if a large area is being treated.
Higher Cost: FUE is typically more expensive than other hair transplant methods like FUT. The higher cost is due to the more labor-intensive nature of the procedure and the specialized skills required to extract and implant individual follicles.
Donor Hair Wastage: There can be a higher rate of graft wastage in FUE compared to FUT. This is because the process of extracting individual follicles can potentially damage them, reducing the number of viable grafts for transplantation.
Limited Suitability: FUE may not be suitable for all patients. For instance, individuals with a tight scalp or those with insufficient donor hair may not be ideal candidates for FUE. Also, FUE might not be the best option for individuals with advanced hair loss, as it may not provide the coverage they need.
Potential for Overharvesting: There’s a risk of overharvesting with FUE, which means too many follicles are removed from the donor area, leading to a thin or patchy appearance. This risk is higher if the procedure is not performed by an experienced surgeon.
Longer Procedure Time: Because FUE involves the extraction of individual follicles, the procedure time can be longer than FUT. This can make the process more tiring for the patient and require more than one session to achieve the desired results.
Variable Results: The success of an FUE procedure can depend on the skill and experience of the surgeon, as well as the patient’s hair characteristics and overall health. Therefore, results can vary, and there’s no guarantee of success.
FUT Pros & Cons
Pros of FUT
FUT allows for the transplantation of a large number of grafts in a single session. This is particularly beneficial for patients who have extensive hair loss and require a significant amount of hair to be transplanted. The ability to transplant a large number of grafts in one session reduces the number of surgeries needed, saving both time and money for the patient.
FUT has a high survival rate of the transplanted hair follicles. This is because the follicular units are extracted as a strip from the back of the scalp, which is a region resistant to balding. The strip is then dissected under a microscope into individual follicular units, ensuring minimal damage to the hair follicles. This meticulous process results in a high survival rate of the transplanted hair, leading to a denser and more natural-looking result.
FUT is cost-effective. Compared to other hair transplant methods, FUT is generally more affordable. This is because it is a less labor-intensive procedure and can transplant a large number of grafts in a single session. Therefore, patients who are on a budget may find FUT to be a more economical option.
FUT leaves a linear scar at the back of the scalp, which can easily be concealed by the patient’s existing hair. Although some patients may view this as a disadvantage, the scar can be minimized by a skilled surgeon and is typically not noticeable unless the patient shaves their head.
FUT has a proven track record. It has been around for decades and has been refined and perfected over the years. Therefore, patients who choose FUT can have confidence in the procedure’s effectiveness and safety.
Cons of FUT
FUT can result in a noticeable scar. The procedure involves removing a strip of scalp from the back of the head, which leaves a linear scar. Although this scar can be concealed by existing hair, it may be visible if the patient has a short haircut or shaves their head. This can be a significant disadvantage for those who prefer to wear their hair short.
FUT involves a longer recovery period. As it is a surgical procedure that involves removing a strip of scalp, patients typically experience more post-operative discomfort and a longer healing time compared to other hair transplant methods. This can be inconvenient for patients who wish to return to their normal activities quickly.
FUT may not be suitable for everyone. Patients with tight or very loose scalps may not be good candidates for FUT. Additionally, those who have undergone previous FUT procedures may not have enough laxity left in their scalps for further strip extractions.
FUT can limit the patient’s hairstyle options. Because of the linear scar left by the procedure, patients may need to keep their hair at a certain length to conceal the scar. This can limit their hairstyle options and may be a disadvantage for those who prefer shorter hairstyles.
FUT can lead to a depletion of the donor supply. Since FUT involves removing a strip of scalp, it can deplete the donor area, especially if multiple procedures are performed. This can limit the number of grafts available for future hair transplant procedures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation) and FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) are effective hair transplant methods, each with its own pros and cons. FUT allows for the transplantation of a large number of grafts in a single session, has a high survival rate of the transplanted hair, is cost-effective, leaves a concealable scar, and has a proven track record. However, it can result in a noticeable scar, involves a longer recovery period, may not be suitable for everyone, can limit hairstyle options, and can lead to a depletion of the donor supply. On the other hand, FUE is less invasive, leaves no linear scar, has a shorter recovery period, and provides more natural-looking results. However, it is more time-consuming, more expensive, and may not be suitable for patients requiring a large number of grafts.
Read More