Gastric bypass and gastric sleeve surgeries are two of the most common types of bariatric surgery, designed to help individuals with severe obesity lose weight and improve their overall health. Both procedures aim to reduce the size of the stomach, but they do so in different ways and have distinct benefits and risks.
What is Gastric Bypass?
Gastric bypass, also known as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, is a type of weight-loss surgery designed to help individuals with severe obesity achieve significant and sustained weight loss. This procedure involves creating a small pouch from the stomach and connecting it directly to the small intestine, effectively bypassing a large portion of the stomach and the first part of the small intestine (the duodenum). This alteration not only reduces the stomach's capacity, limiting the amount of food one can eat at a time, but also changes the way the body absorbs nutrients and calories.
The surgery begins with the surgeon dividing the stomach into two sections: a small upper pouch and a much larger lower remnant. The small pouch, which can hold only about an ounce of food, is then connected to a segment of the small intestine. This new configuration allows food to bypass the majority of the stomach and the upper part of the small intestine, leading to reduced calorie absorption.
One of the primary benefits of gastric bypass surgery is its effectiveness in promoting significant weight loss. Patients typically lose 60-80% of their excess body weight within the first two years following the procedure. This weight loss can lead to substantial improvements in obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, and joint pain. In many cases, patients experience a complete remission of type 2 diabetes shortly after surgery, even before significant weight loss occurs.
However, gastric bypass is not without risks and potential complications. The surgery is more complex than other weight-loss procedures, such as gastric sleeve surgery, and carries a higher risk of complications. These can include infections, blood clots, and nutritional deficiencies due to the altered digestive process. Patients must commit to lifelong dietary changes and take vitamin and mineral supplements to prevent deficiencies. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to monitor nutritional status and overall health.
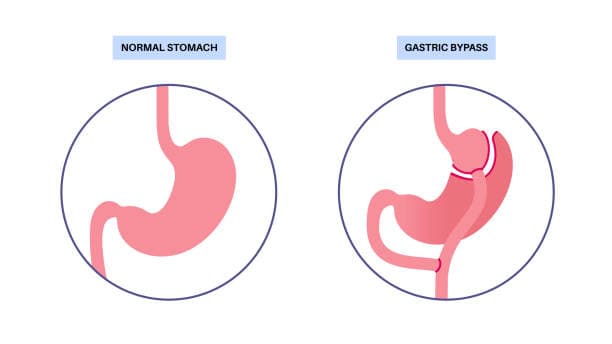
Gastric Bypass Pros & Cons
Gastric bypass surgery, is a popular and effective weight-loss procedure, but it comes with both advantages and disadvantages that should be carefully considered.
Pros of Gastric Bypass
One of the primary benefits of gastric bypass surgery is its effectiveness in promoting significant and sustained weight loss. Patients typically lose 60-80% of their excess body weight within the first two years following the procedure.
This substantial weight loss can lead to dramatic improvements in obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, and joint pain. In many cases, patients experience a complete remission of type 2 diabetes shortly after surgery, even before significant weight loss occurs.
Additionally, gastric bypass surgery can improve overall quality of life, increasing mobility, and reducing the risk of developing serious health conditions associated with obesity, such as heart disease and stroke.
Another advantage is the standardized surgical technique, which has been refined over decades, leading to predictable outcomes and a relatively high success rate.
The procedure also alters the digestive process, which can help patients develop healthier eating habits and reduce their overall calorie intake.
Cons of Gastric Bypass
Despite its benefits, gastric bypass surgery is not without risks and potential complications. The procedure is more complex than other weight-loss surgeries, such as gastric sleeve surgery, and carries a higher risk of complications.
Complications can include infections, blood clots, and adverse reactions to anesthesia.
One of the significant long-term risks is nutritional deficiencies, as the surgery alters the digestive process, leading to reduced absorption of essential nutrients such as vitamins B12, D, iron, and calcium. Patients must commit to lifelong dietary changes and take vitamin and mineral supplements to prevent deficiencies.
Another potential downside is the possibility of developing dumping syndrome, a condition where food moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine, causing symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and dizziness.
Additionally, some patients may experience weight regain over time if they do not adhere to the recommended lifestyle changes and dietary guidelines.
The recovery period for gastric bypass surgery can also be longer compared to less invasive procedures, requiring a significant commitment to follow-up care and lifestyle adjustments. Patients need to attend regular medical appointments to monitor their health and nutritional status, which can be time-consuming and require ongoing effort.
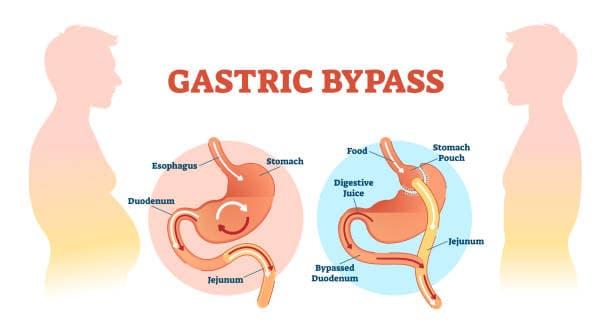
What is a Gastric Sleeve?
Gastric sleeve surgery, also known as sleeve gastrectomy, is a type of bariatric (weight-loss) surgery designed to help individuals with severe obesity achieve significant and sustained weight loss. This procedure involves removing approximately 80% of the stomach, leaving behind a narrow, tube-shaped section that resembles a sleeve or banana. By significantly reducing the size of the stomach, gastric sleeve surgery limits the amount of food that can be consumed at one time, promoting a feeling of fullness with smaller meals and thereby reducing overall calorie intake.
The surgery is typically performed laparoscopically, which means it involves small incisions and the use of a camera and specialized instruments. This minimally invasive approach generally results in shorter recovery times, less postoperative pain, and reduced risk of complications compared to open surgery. During the procedure, the surgeon removes the outer curved part of the stomach, creating a new stomach pouch that is much smaller in volume. This new stomach pouch not only restricts food intake but also reduces the production of ghrelin, a hormone that stimulates hunger, which can help decrease appetite and support weight loss efforts.
One of the primary benefits of gastric sleeve surgery is its effectiveness in promoting significant weight loss. Patients typically lose about 50-70% of their excess body weight within the first two years following the procedure. This weight loss can lead to substantial improvements in obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, and joint pain. Many patients experience a marked improvement in their overall quality of life, including increased mobility and energy levels.
However, gastric sleeve surgery is not without risks and potential complications. As with any major surgery, there are risks of infection, bleeding, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. Long-term risks include nutritional deficiencies, as the reduced stomach size can limit the absorption of essential nutrients. Patients must commit to lifelong dietary changes and take vitamin and mineral supplements to prevent deficiencies. Additionally, there is a risk of developing gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or experiencing a narrowing of the stomach sleeve, which may require further medical intervention.
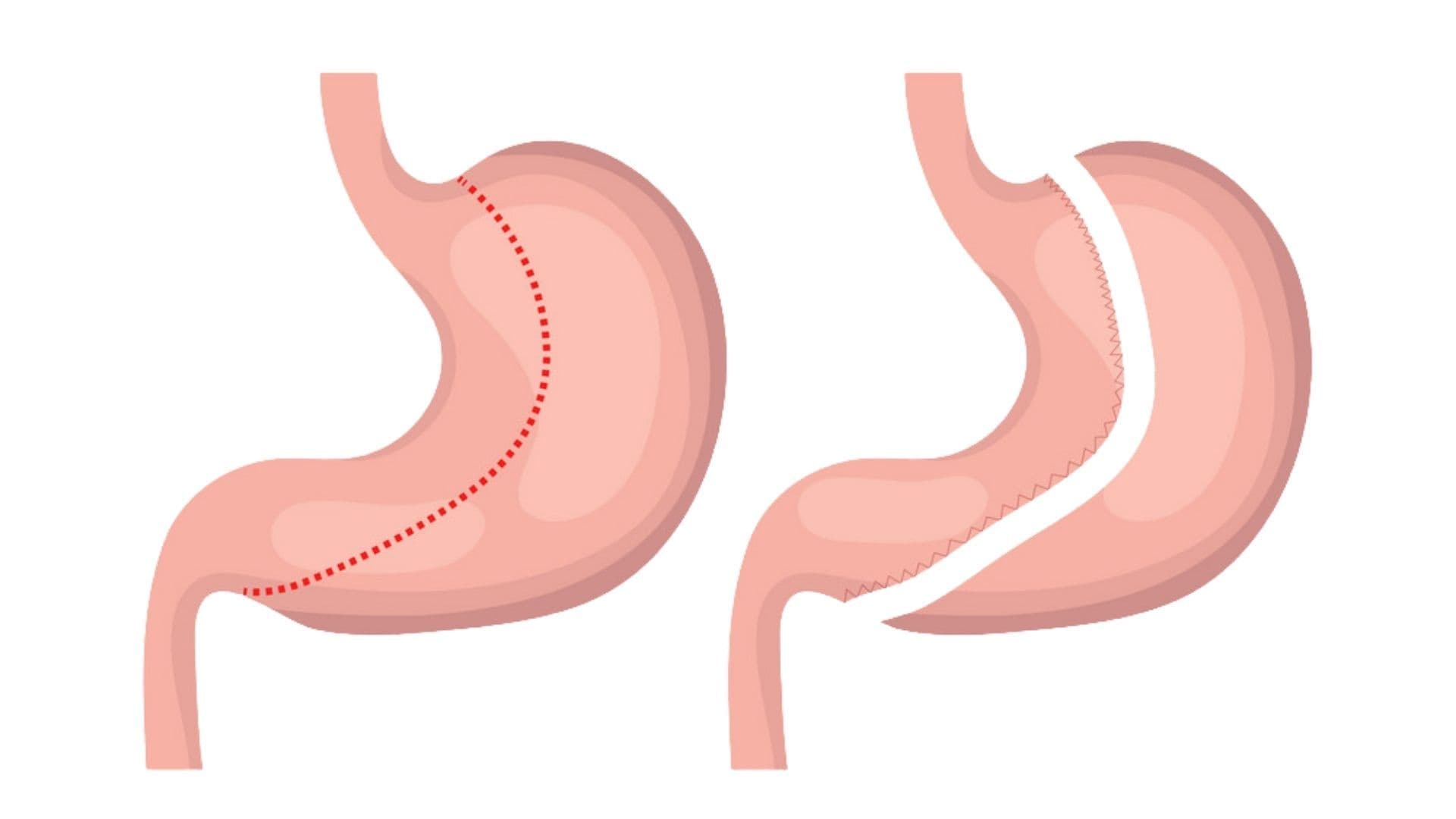
Gastric Sleeve Pros & Cons
Gastric sleeve surgery, is a popular bariatric procedure designed to help individuals with severe obesity achieve significant weight loss. While gastric sleeve surgery offers numerous benefits, it also comes with potential drawbacks that should be carefully considered.
Pros of Gastric Sleeve
One of the primary advantages of gastric sleeve surgery is its effectiveness in promoting substantial weight loss. Patients typically lose about 50-70% of their excess body weight within the first two years following the procedure.
This significant weight loss can lead to improvements in obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, and joint pain. Many patients experience enhanced mobility, increased energy levels, and an overall better quality of life.
Another benefit of gastric sleeve surgery is that it is a relatively simpler procedure compared to other bariatric surgeries, such as gastric bypass. It does not involve rerouting the intestines, which reduces the risk of complications and shortens the recovery time. The minimally invasive laparoscopic approach used in most gastric sleeve surgeries also results in smaller incisions, less postoperative pain, and quicker healing.
Additionally, gastric sleeve surgery has a lower risk of long-term nutritional deficiencies compared to gastric bypass, as it does not alter the absorption of nutrients in the intestines. Patients still need to adhere to a healthy diet and take vitamin supplements, but the risk of severe deficiencies is generally lower.
Cons of Gastric Sleeve
Despite its benefits, gastric sleeve surgery is not without risks and potential complications.
As with any major surgery, there are risks of infection, bleeding, and adverse reactions to anesthesia.
Long-term risks include the possibility of developing gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or experiencing a narrowing of the stomach sleeve, which may require further medical intervention.
Another potential downside is that while gastric sleeve surgery is effective for weight loss, it may not lead to as rapid or significant weight loss as gastric bypass. Some patients may also experience weight regain over time if they do not adhere to the recommended lifestyle changes and dietary guidelines.
Additionally, gastric sleeve surgery is irreversible, meaning that once the stomach is removed, it cannot be restored to its original size. This permanent change requires a lifelong commitment to healthy eating habits and regular follow-up care to ensure long-term success and health.

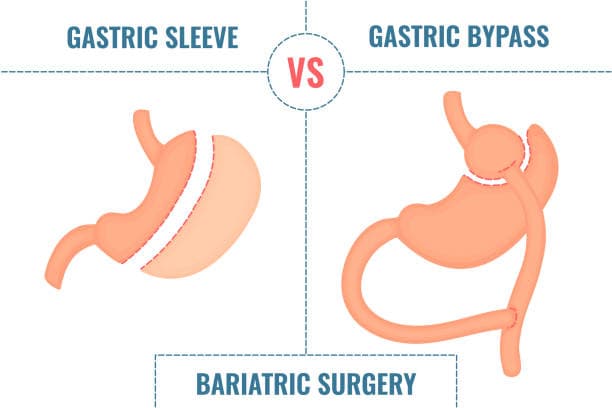
Gastric Bypass vs. Gastric Sleeve; which is right for me?
Gastric bypass and gastric sleeve are two of the most common bariatric surgeries designed to help individuals with severe obesity achieve significant weight loss. While gastric sleeve surgery is generally simpler and has fewer complications, gastric bypass may lead to more substantial and longer-lasting weight loss and better control of blood sugar levels. Both surgeries are effective in achieving significant weight loss and improving obesity-related conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea. The choice between gastric bypass and gastric sleeve surgery depends on various factors, including the patient's health status, weight loss goals, and personal preferences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both gastric bypass and gastric sleeve surgeries are effective bariatric procedures that offer significant weight loss and improvements in obesity-related conditions. Both surgeries require a lifelong commitment to dietary changes, regular follow-up care, and lifestyle adjustments to ensure long-term success and health.
Read More