Hair restoration techniques have evolved significantly over the years, with two prominent methods being hair transplants and hair plugs. While both procedures aim to address hair loss and promote hair growth, they differ in their techniques and outcomes.
Hair Transplant vs. Hair Plugs
Hair transplants and hair plugs are two methods used to address hair loss, but they differ significantly in technique and results. Hair plugs were an early form of hair restoration, popular in the mid-20th century. This method involved transplanting large, round sections of hair-bearing scalp, known as plugs, from the donor area to the balding areas. Each plug contained multiple hair follicles, resulting in a clumpy and often unnatural appearance. Over time, the limitations of hair plugs, such as noticeable scarring and unnatural hair patterns, led to the development of more advanced techniques. Hair transplants, including Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE), involve transplanting individual hair follicles or small groups of follicles from the donor area to the recipient area. These modern techniques result in a more natural-looking hairline, minimal scarring, and overall better aesthetic outcomes compared to hair plugs.

What is a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure designed to restore hair in areas affected by baldness or thinning. This procedure involves moving hair follicles from a donor area, typically the back or sides of the scalp where hair is more resistant to balding, to the recipient area, which is usually the balding or thinning part of the scalp. The goal of a hair transplant is to achieve a natural-looking hairline and fill in areas with sparse hair, ultimately improving the patient’s appearance and confidence.
There are two main methods of hair transplantation: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). In FUT, a strip of scalp is removed from the donor area, and the individual hair follicles are dissected from this strip and transplanted to the recipient area. This method can leave a linear scar at the donor site, but it allows for the transplantation of a large number of grafts in a single session. On the other hand, FUE involves extracting individual hair follicles directly from the donor area using a small punch tool. These follicles are then implanted into the recipient area. FUE is less invasive than FUT and leaves minimal scarring, making it a popular choice among patients.
The procedure begins with a thorough consultation with a hair restoration specialist to assess the patient’s hair loss pattern, discuss their goals, and determine the most suitable method1. On the day of the surgery, the patient’s scalp is cleaned, and local anesthesia is administered to numb the donor and recipient areas. The surgeon then performs the extraction and implantation of hair follicles, which can take several hours depending on the number of grafts needed. Patients are usually awake during the procedure and can watch TV or listen to music to pass the time.
After the surgery, patients may experience mild discomfort, swelling, and redness in the treated areas. Small scabs may form around the transplanted follicles, which typically heal within a week or two. It is normal for the transplanted hair to shed within the first few weeks, but new hair growth usually begins within a few months. Full results can take 6 to 12 months to become apparent, as the transplanted hair grows at a rate similar to natural hair.
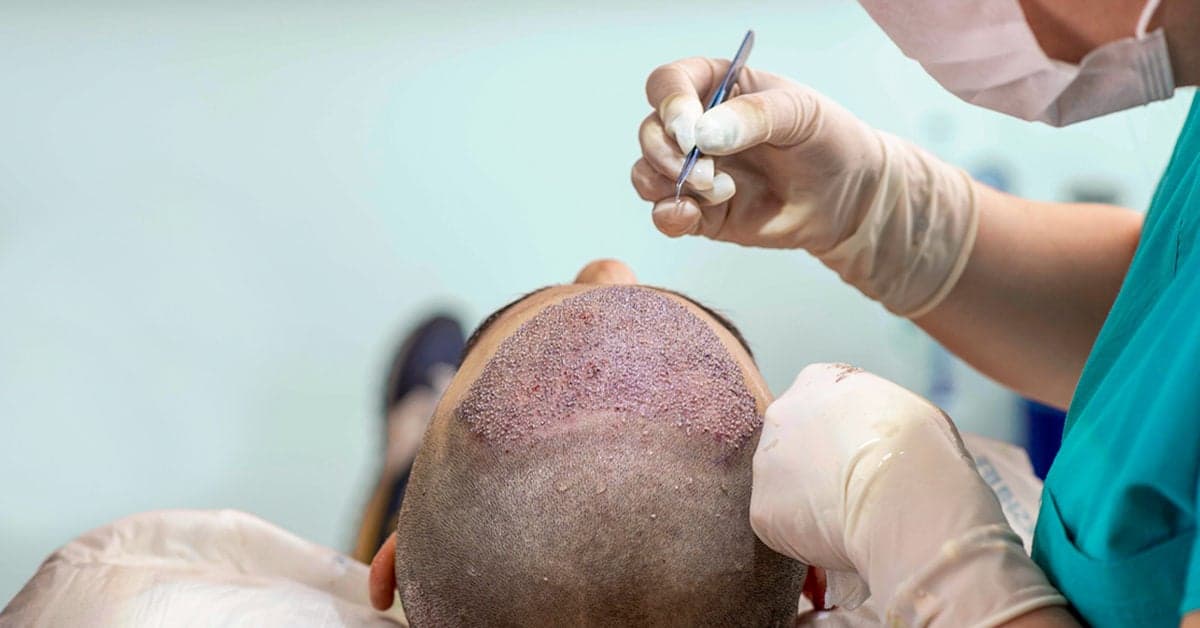
Hair Transplant Pros & Cons
Hair transplants are a popular solution for individuals experiencing hair loss, offering both advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these pros and cons can help individuals make informed decisions about whether this procedure is right for them.
Pros of Hair Transplant
Natural Results: One of the primary benefits of hair transplants is the natural-looking results they provide. Modern techniques, such as Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE), involve transplanting individual hair follicles or small groups of follicles, resulting in a more natural hairline and overall appearance.
Permanent Solution: Hair transplants offer a long-lasting solution to hair loss. The transplanted hair follicles are typically resistant to balding, meaning the results can be permanent. This makes hair transplants a more durable option compared to temporary treatments like topical solutions or wigs.
Improved Self-Esteem: Many individuals who undergo hair transplants report a significant boost in self-esteem and confidence. Restoring a fuller head of hair can improve one’s appearance and positively impact their overall quality of life.
Minimally Invasive: Hair transplant procedures are relatively low-risk and minimally invasive compared to other surgical procedures. They are typically performed under local anesthesia, and patients can often return home the same day.
Cons of Hair Transplant
Cost: One of the main drawbacks of hair transplants is the cost. The procedure can be expensive, depending on the extent of the transplant and the surgeon’s expertise. Additionally, because hair transplants are considered cosmetic procedures, they are not typically covered by health insurance.
Multiple Sessions: Depending on the extent of hair loss and the desired results, multiple sessions may be required to achieve the desired outcome. This can increase the overall cost and time commitment for the patient.
Recovery Time: While hair transplants are minimally invasive, they do require a recovery period. Patients may experience redness, swelling, and scabbing in the treated areas, which can take several days to weeks to heal. It is essential to follow post-operative care instructions to ensure proper healing and minimize the risk of complications.
Potential Risks and Side Effects: Like any surgical procedure, hair transplants come with potential risks and side effects. These can include infection, bleeding, scarring, and unnatural-looking hair growth if not performed by a skilled surgeon. It is crucial to choose an experienced and reputable surgeon to minimize these risks.
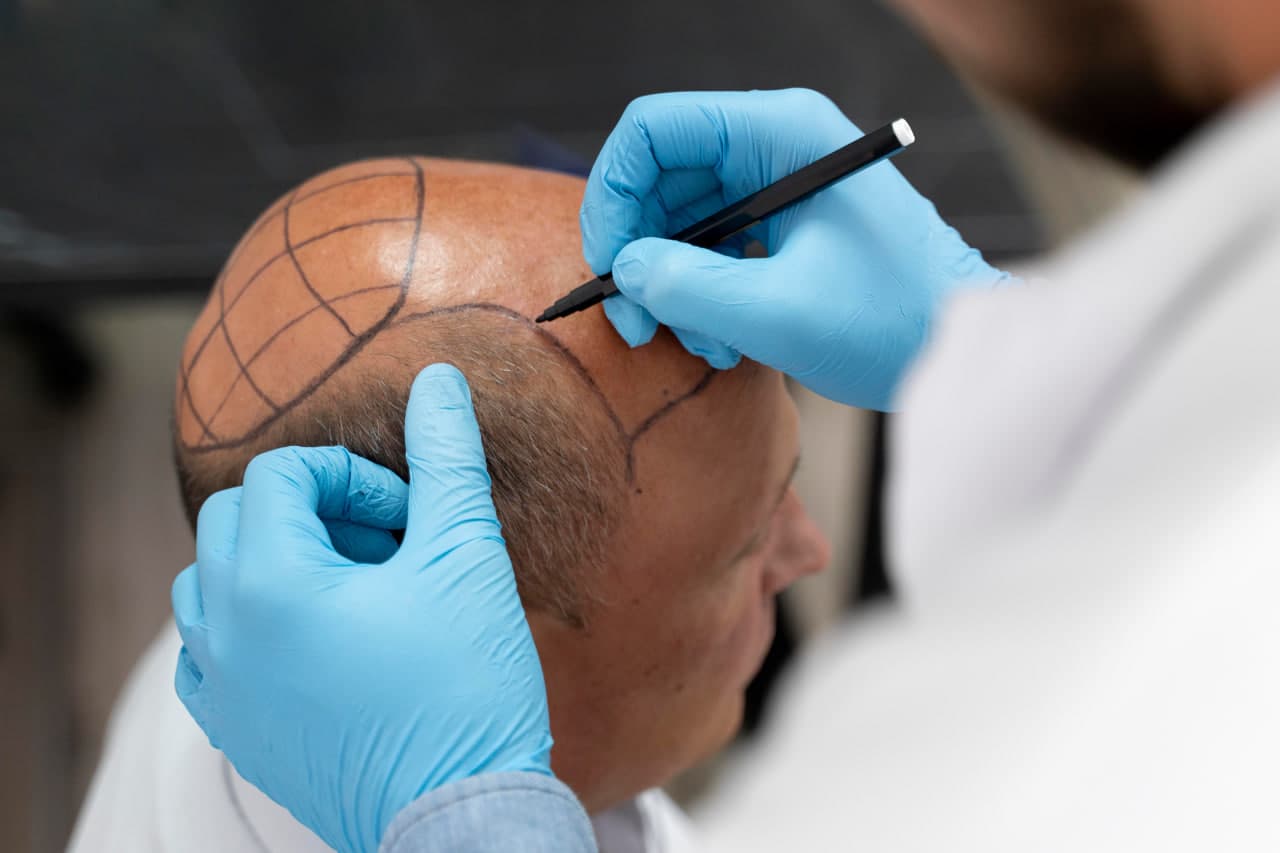
What are Hair Plugs?
Hair plugs were an early form of hair transplantation used to address hair loss and promote hair regrowth. This technique was popularized in the 1950s and continued to be used until the early 2000s. The procedure involved extracting round sections of hair-bearing skin, known as plugs, from the donor area, typically the back or sides of the scalp, and transplanting them into balding areas. Each plug contained multiple hair follicles, usually ranging from one to eight units of hair. The primary goal of hair plugs was to cover balding areas and create a fuller head of hair.
The process of hair plug transplantation began with the surgeon using a punch tool to remove the plugs from the donor area. These plugs, which were about 4 millimeters (0.16 inches) in diameter, were then inserted into small incisions made in the recipient area. The procedure was relatively straightforward, but it had several limitations. One of the main drawbacks of hair plugs was the unnatural appearance they often produced. Because the plugs were relatively large and contained multiple hair follicles, the transplanted hair tended to grow in clumps, creating a “doll-like” or “cornrow” effect. This unnatural look was a significant concern for many patients and led to dissatisfaction with the results.
Over time, advancements in hair transplantation techniques led to the development of more refined methods, such as Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). These modern techniques involve transplanting individual hair follicles or small groups of follicles, known as follicular units, from the donor area to the recipient area.
As a result of these advancements, hair plugs have become obsolete and are no longer performed. The newer techniques offer several advantages, including quicker procedure times, a lower risk of scarring, and more natural results. Patients seeking hair restoration today are more likely to opt for FUT or FUE, which provide superior outcomes compared to the older hair plug method.
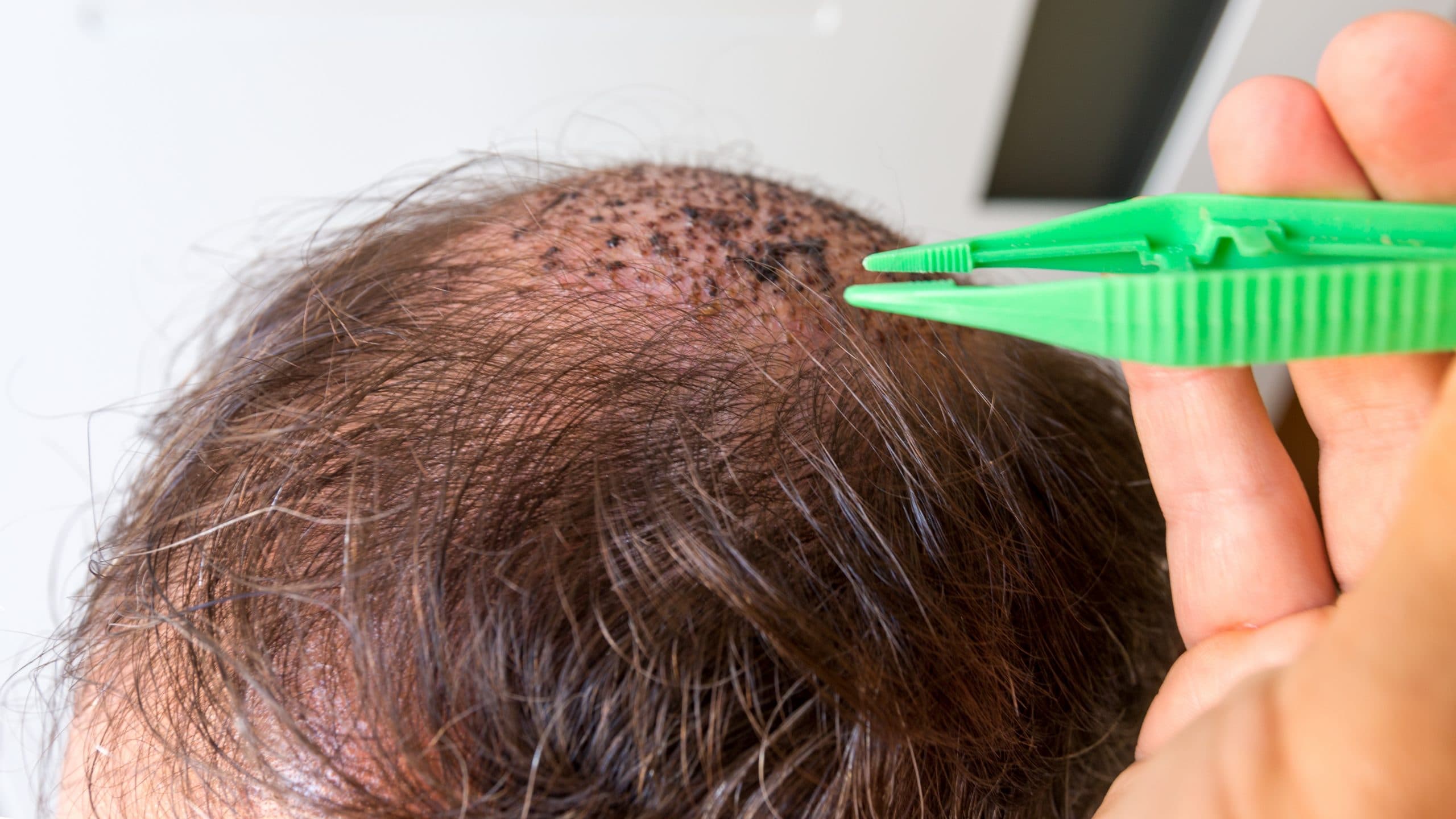
Hair Plugs Pros & Cons
Hair plugs, an early form of hair transplantation, were widely used from the 1950s until the early 2000s to address hair loss. While they offered a solution for balding areas, they came with both advantages and disadvantages.
Pros of Hair Plugs
Cost-Effective: One of the main advantages of hair plugs was their relatively lower cost compared to modern hair transplant techniques. This made them accessible to a broader range of individuals seeking hair restoration.
Coverage for Larger Areas: Hair plugs could provide coverage for larger areas of baldness in a single session. This was particularly beneficial for individuals with extensive hair loss, as it allowed for more significant coverage in a shorter amount of time.
Early Availability: When hair plugs were popular, they were one of the few available options for hair restoration. This made them a pioneering solution for those suffering from hair loss.
Cons of Hair Plugs
Unnatural Appearance: One of the most significant drawbacks of hair plugs was the unnatural appearance they often produced. Because the plugs were relatively large and contained multiple hair follicles, the transplanted hair tended to grow in clumps, creating a “doll-like” or “cornrow” effect. This unnatural look was a major concern for many patients and led to dissatisfaction with the results.
Scarring: The use of large punch tools to extract and transplant the plugs often resulted in noticeable scarring at both the donor and recipient sites. These scars could be difficult to conceal and were a common complaint among patients.
Risk of Complications: Hair plugs came with a higher risk of complications compared to modern techniques. These complications included infection, bleeding, and poor healing, which could further impact the overall results and patient satisfaction.
Limited Refinement: Unlike modern techniques such as Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE), hair plugs lacked the refinement needed to create a natural-looking hairline. The large size of the plugs made it challenging to achieve the delicate and precise placement required for a seamless appearance.
Obsolescence: As advancements in hair restoration techniques emerged, hair plugs became obsolete. Modern methods like FUT and FUE offer superior results, minimal scarring, and quicker recovery times, making them the preferred choice for hair restoration today.
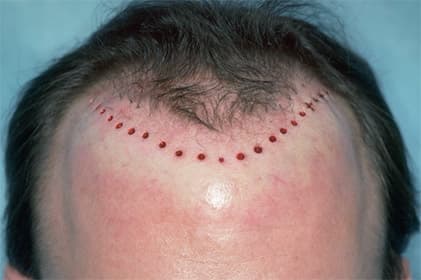
The Difference Between Hair Transplants & Plugs
Hair transplants and hair plugs are two methods used to address hair loss, but they differ significantly in their techniques and outcomes. Hair plugs were an early form of hair restoration, popularized in the mid-20th century. This method involved using a large punch tool to remove round sections of hair-bearing scalp from the donor area and transplanting them to the balding areas. Each plug contained multiple hair follicles, resulting in a clumpy and often unnatural appearance. In contrast, modern hair transplants include techniques like Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE), which involve transplanting individual hair follicles or small groups of follicles from the donor area to the recipient area. FUT involves removing a strip of scalp and dissecting it into individual follicular units, while FUE involves extracting individual follicles directly from the scalp. These modern techniques result in a more natural-looking hairline and minimal scarring.
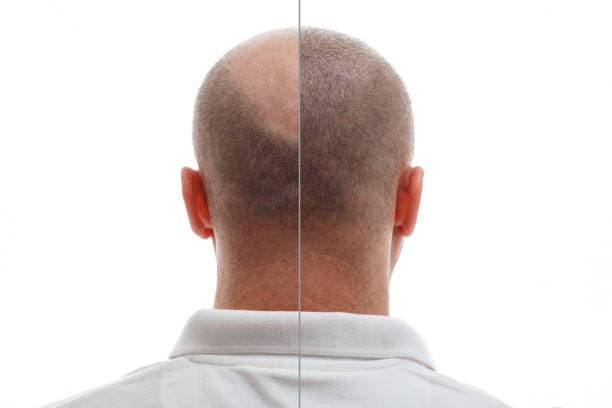

Conclusion
In conclusion, while hair plugs were an early attempt at hair restoration, they have largely been replaced by modern hair transplant techniques due to their superior results and less invasive nature. Hair plugs involved transplanting large sections of hair-bearing scalp, which often resulted in an unnatural, clumpy appearance and noticeable scarring. In contrast, modern hair transplants, such as Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE), involve transplanting individual hair follicles or small groups of follicles, resulting in a more natural-looking hairline and minimal scarring. These advancements have significantly improved aesthetic outcomes and overall patient satisfaction, making hair transplants the preferred choice for those seeking effective and natural hair restoration solutions. Understanding these differences can help individuals make informed decisions about their hair restoration options and achieve the best possible results.
Read More