Gynecomastia refers to a condition where the breast tissue in men or boys overdevelops & enlarges. As preteens or teenage boys go through hormonal changes their breasts may become larger, growing unevenly. But it can also happen to newborn babies and men as they age.
What is gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is a common condition which results in enlarged male breast tissue. This condition may affect newborns, boys going through puberty, and older adults. Although there are many causes for gynecomastia, the most common is an imbalance of testosterone and estrogen hormones.
How does gynecomastia affect my body?
Gynecomastia will cause a growth underneath the nipple. Which can be seen as a breast lump or felt when you press on the area. These breast lumps or enlargements may occur in one or both breasts. You may feel tender to touch in your breast.
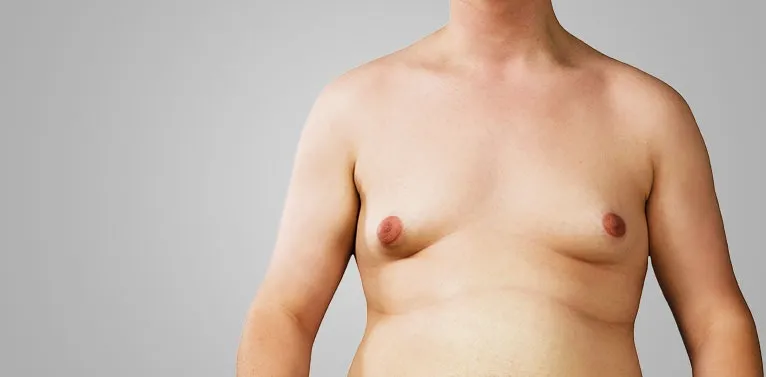
What causes gynecomastia?
Most gynecomastia is caused by hormonal changes while other causes are unknown. Gynecomastia is usually a benign (noncancerous) condition. This happens when an imbalance between estrogen and testosterone occurs in the body. Gynecomastia can be a side effect of certain medicines, such as antidepressants, antibiotics, chemotherapy, prostate cancer medicines, ulcer or cardiovascular medicines. Some diseases and medical conditions may also cause gynecomastia. These include:
Liver diseases
Kidney disease
Lung cancer
Testicular cancer
Tumors of the adrenal glands or pituitary gland
Some conditions that a baby is born with (congenital disorders)
Thyroid disorders
Injury or trauma
Obesity
Who might have gynecomastia?
Birth: In more than half of newborn males, caused by their mother’s estrogen levels a breast enlargement may occur. The enlarged breasts usually go away within a few weeks.
Puberty: Due to an imbalance in testosterone and estrogen hormones during teenage years, more than half the boys have some degree of breast enlargement. The condition goes away as hormone levels even out; which may take about six months to two years to complete.
Adulthood: As men age, their bodies will produce less testosterone, which is the reason for breast enlargement in men over 50. They may also have more body fat, which stimulates estrogen production and breast tissue growth.
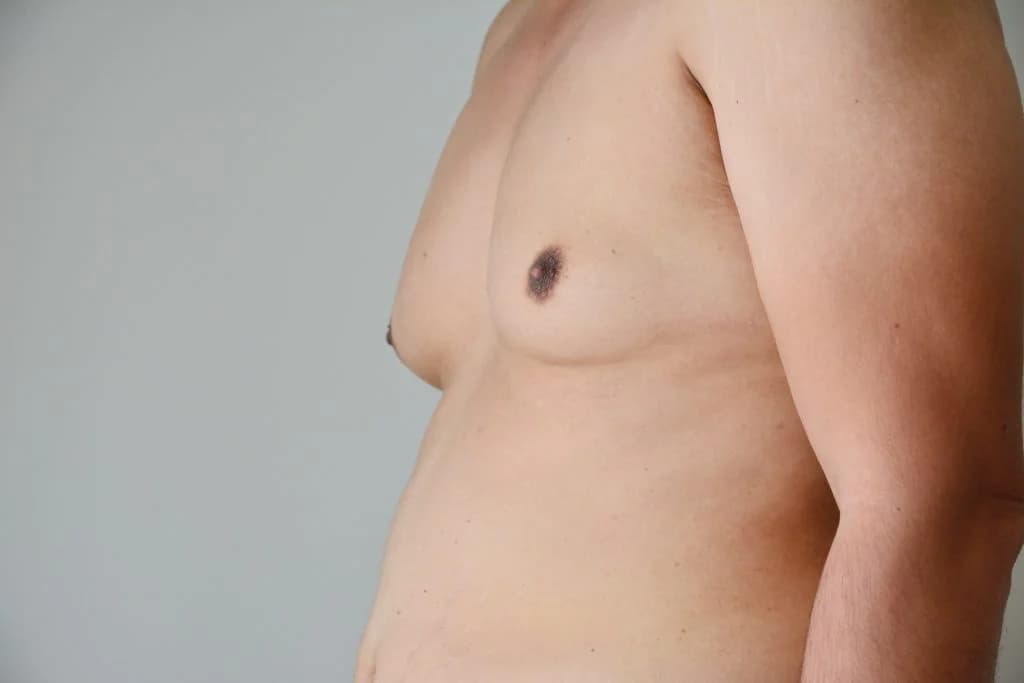
How is gynecomastia diagnosed?
For gynecomastia to be diagnosed, your doctor will need to give you a physical exam as well as go through your medical history. To rule out other diseases or conditions, you may also have tests including:
Blood tests, including liver function tests and hormone studies.
Urine tests
A low-dose X-ray of your breast (mammogram)
A small breast tissue sample (a biopsy) may be removed and checked for cancer cells.
How is gynecomastia treated?
Based on your age, your overall health, your ability to handle medications and treatments, as well as your treatment option of choice, your healthcare provider will figure out the best treatment for you. In most cases, gynecomastia regresses within two years and requires no treatment. Treatments for gynecomastia include:
Non-surgical treatments for gynecomastia
In some cases, gynecomastia will go away on its own in a few months. But there are also a few things your doctor may suggest to help with your gynecomastia. As well as encouraging patients to exercise, reduce alcohol, and avoid narcotic drugs and marijuana.
Medications
Although these are not approved treatments, your doctor may suggest these medications for gynecomastia treatment:
Testosterone replacement therapy
Clomiphene
Tamoxifen (Nolvadex), a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM)
Danazol
Diet changes
It is believed that certain foods can lead to a shift in hormone levels, which include:
Canned food
Soy
Shrimps
Beer
Protean powders
Strawberries
Multigrain bread
Instead, patients are encouraged to eat a low-calorie, nutrient-rich diet.
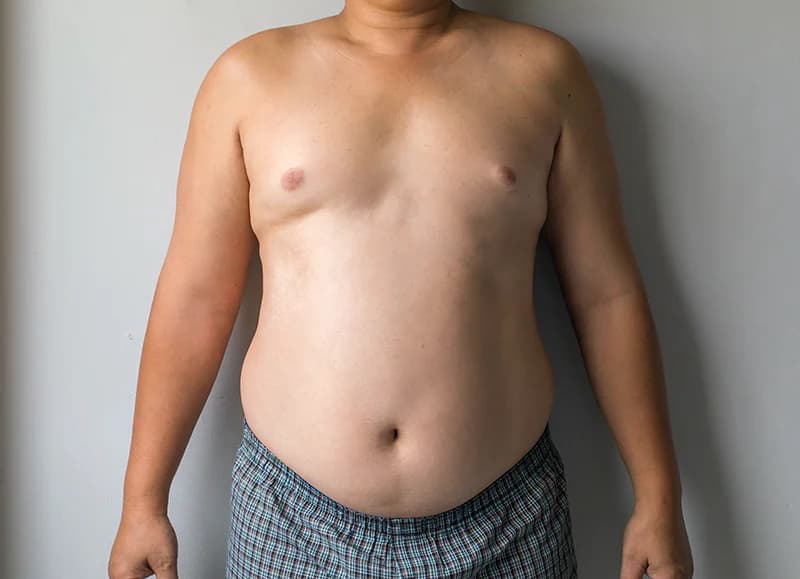
Surgical treatments for gynecomastia
Although some patients reach their desired goals with the non-surgical treatments for gynecomastia or simply don’t want to have surgery; in some cases, surgery may be recommended by your doctor. There are two main surgical techniques for gynecomastia surgery. Your doctor will give you an examination and determine the best option for you. The surgical approaches to gynecomastia removal are:
Liposuction
Liposuction is a common treatment for gynecomastia. In cases where breast enlargement results from the accumulation of fat cells, this is the best treatment. During the procedure, a thin tube will be inserted through an incision on the chest, which will remove excess fat by vacuum suction. A gynecomastia liposuction is done under local anesthesia.
Excision technique
This procedure is best for cases where excess skin needs to be removed. This technique may involve reducing the areola and repositioning the nipple. During this method, incisions will be made in the breasts to access and remove the excess tissue. As the excision technique is an outpatient procedure, you won’t need to stay in the hospital overnight.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the treatment of enlarged male breast tissue, or gynecomastia, is tailored to the individual’s needs and may involve lifestyle changes, medication, or surgery. Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight and reducing alcohol consumption can sometimes help reduce the size of the breast tissue. Medications may be used to address any underlying conditions contributing to gynecomastia. In cases where the enlargement is significant or causing discomfort, surgery may be considered. This can involve liposuction or mastectomy procedures. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to understand the best treatment options for you. Remember, each person’s journey with gynecomastia is unique, and treatment should be a collaborative decision made with your healthcare provider.
Read more: