LASIK eye surgery is the most commonly performed laser refractive surgery to correct vision problems. Laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) can be an alternative to glasses or contact lenses. A refractive error is when your eye does not refract (bend) light properly. LASIK uses a special type of cutting laser to precisely change the shape of the dome-shaped clear tissue at the front of your eye (cornea) to improve vision.
What is LASIK surgery correct?
LASIK surgery may be an option for the correction of one of these vision problems:
Nearsightedness (myopia): If the eyeball is slightly longer than normal or the cornea curves too sharply, light rays focus in front of the retina and blur distant vision. Making it difficult to see objects far away but the close ones fairly clearly.
Farsightedness (hyperopia): If the eyeball is shorter than average or the cornea is too flat, light focuses behind the retina instead of on it. Making the near vision, and sometimes distant vision, blurry.
Astigmatism: When the cornea curves or flattens unevenly, the result is astigmatism, which disrupts the focus of near and distant vision.
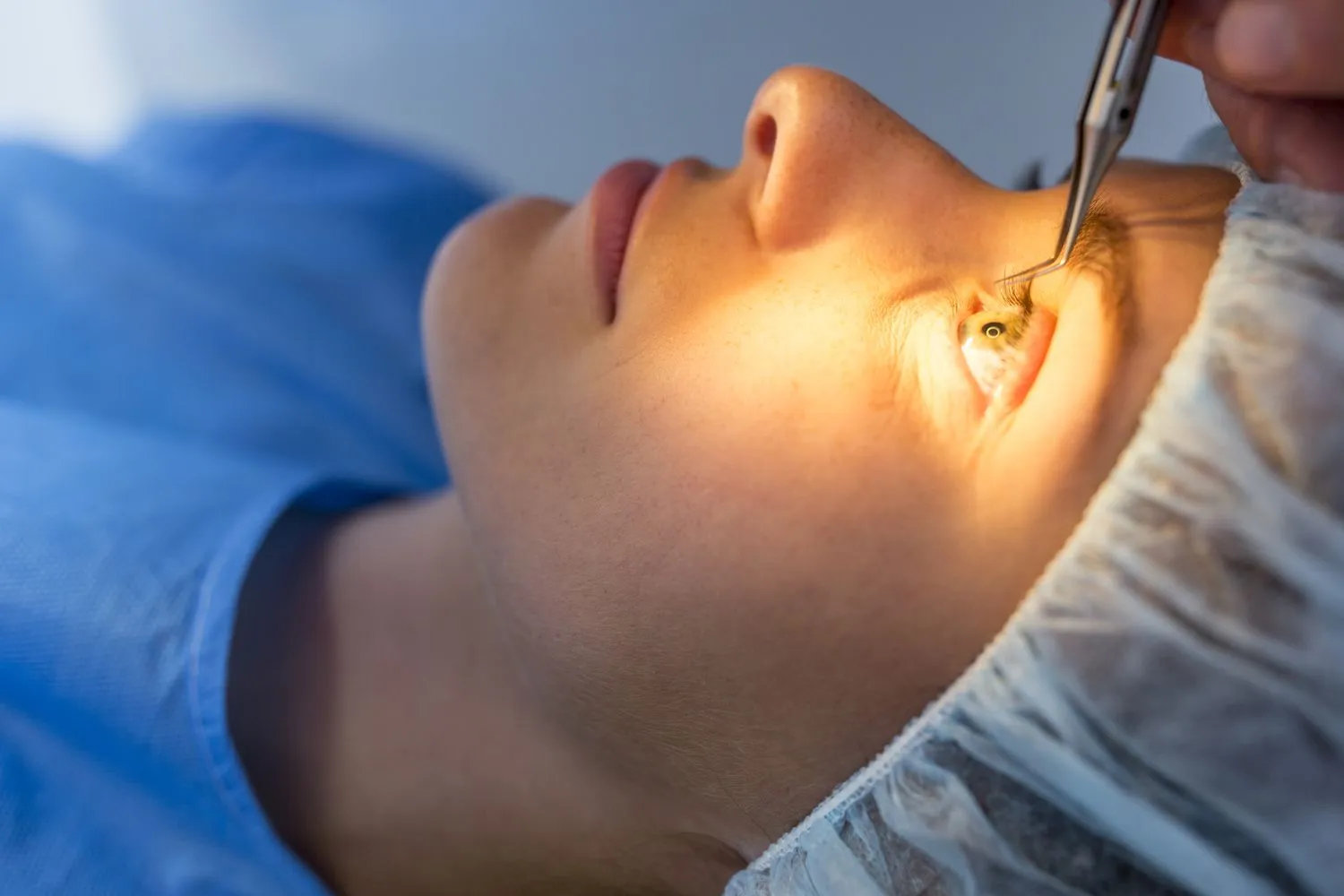
Who Is a Good Candidate for LASIK Surgery?
A good candidate for LASIK surgery must have certain requirements. Such as:
Being 18 years or older (ideally, over 21 years old, since your vision has likely stopped changing)
Your eye prescription should not have changed much in the last year
Your refractive error must be one that can be treated with LASIK
Your corneas need to be thick enough and healthy, and your overall eye health must be generally good
You need to have realistic expectations about what LASIK can and cannot do for you
Some people are not candidates for LASIK. They include people with:
an unstable (changing) refractive error
extreme levels of myopia, hyperopia, or astigmatism
severe dry eye
corneas that are too thin
corneal scars or disease
keratoconus (cone-shaped cornea)
advanced glaucoma
a cataract affecting vision
a history of having certain eye infections
diabetes that is not controlled well
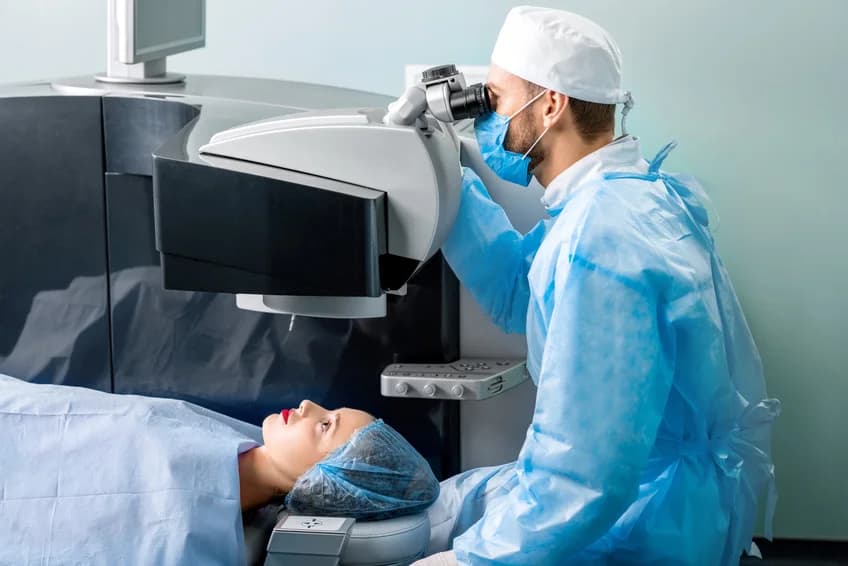
What are the pros and cons of LASIK surgery?
LASIK surgery is generally safe and offers a quick recovery time, but there are risks associated with any surgery you may receive. So, it’s important to understand the possible pros, cons, and effects relating to this surgery.
What are the pros of LASIK surgery?
Safe & effective: LASIK has a high success rate and has been performed for over 20 years. Although there are always risks with surgery, you can rest easier knowing many have found long-term solutions for their refractive errors.
Quick recovery: One of LASIK’s largest benefits is its quick recovery time. Patients witness immediate improvements to their vision and recovery time can be as short as 24 to 48 hours.
No more glasses or contacts: The whole point of having LASIK surgery is to have a lens-free vision.
What are the cons of LASIK surgery?
Potential side effects: There are minor side effects related to LASIK surgery, but many are temporary and only a potential annoyance. Some common side effects include Dry eye, glare & halos. A dry eye may last as long as six months. You can also experience glare and halos after surgery, especially when driving at night.
Potential complications: There are potential complications with any surgery and LASIK is no different, however, these are very rare. Some potential issues with LASIK surgery include Under-corrections, Over-corrections, Astigmatism, and Flap problems.
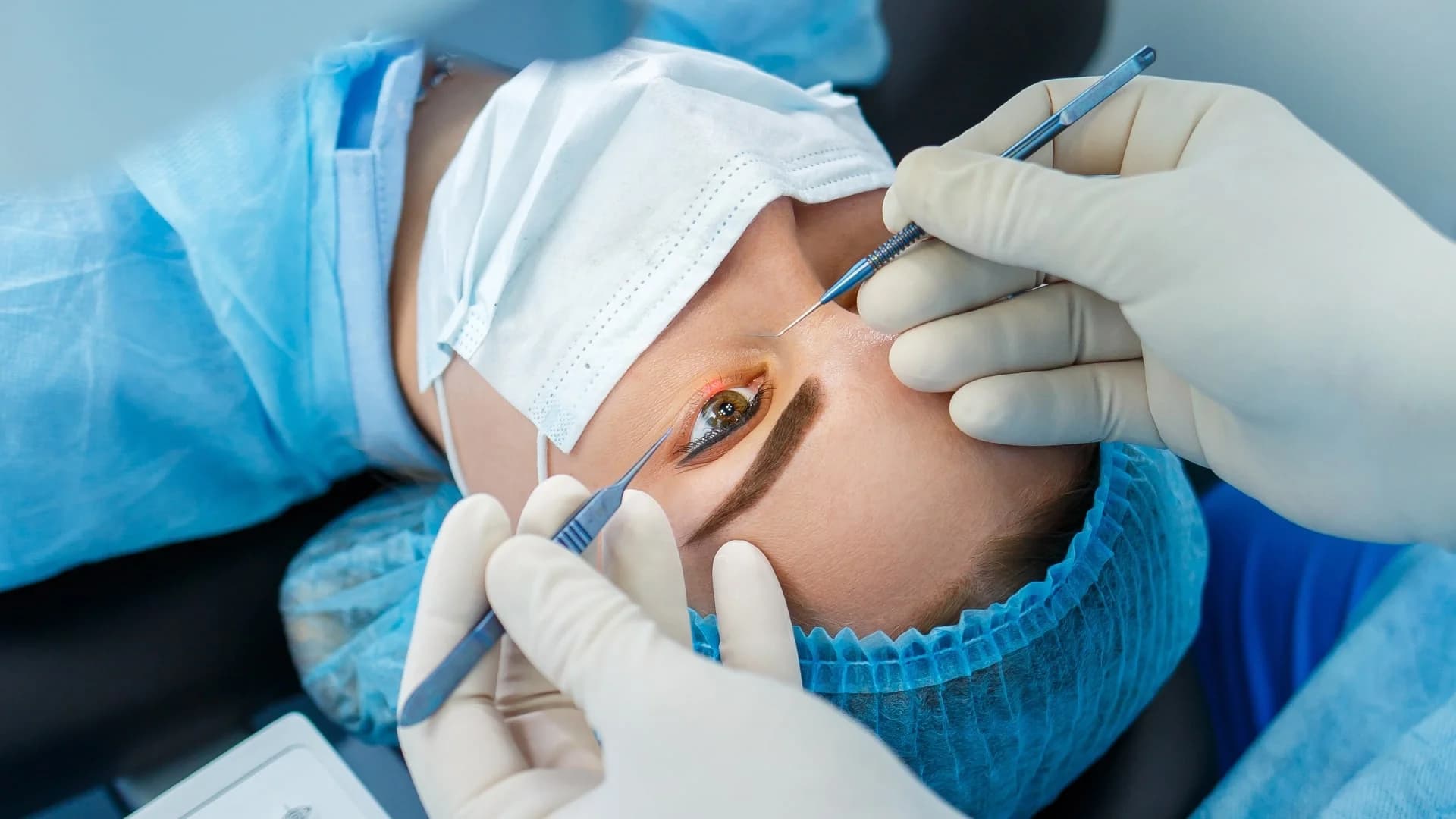
What are the risks of LASIK surgery?
Complications that result in a loss of vision are very rare. But certain risks of LASIK surgery include:
Dry eyes: LASIK surgery causes a temporary decrease in tear production. For the first six months or so after your surgery, your eyes may feel unusually dry as they heal. Dry eyes can reduce the quality of your vision. In case your dry eyes worsen, your doctor might recommend eyedrops.
Glare, halos, and double vision: You may have difficulty seeing at night after surgery, which usually lasts a few days to a few weeks. Also, increased light sensitivity, glare, halos around bright lights, or double vision are common.
Undercorrections: If the laser removes too little tissue from your eye, you won't get the clearer vision results you were hoping for. That is more common for nearsighted people.
Overcorrections: It's also possible that the laser will remove too much tissue from your eye.
Astigmatism: This can be caused by uneven tissue removal. It may require additional surgery, glasses, or contact lenses.
Flap problems: Folding back or removing the flap from the front of your eye during surgery can cause complications, including infection and excess tears.
Regression: When your vision slowly changes back toward your original prescription.
Vision loss or changes: Rarely, surgical complications can result in loss of vision.
LASIK surgery recovery time
Even though patients will be able to see after surgery, it takes 3-6 months for the eye to heal fully. You should avoid strenuous contact sports for at least 4 weeks as well as avoiding swimming for 1-2 months. Also, to avoid any infection, wait 2 weeks before starting to use any cosmetic products around the eyes.
Conclusion
LASIK (Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis) is a popular eye surgery that corrects vision in people who are nearsighted, farsighted, or have astigmatism. The procedure is quick, usually taking less than 30 minutes, and most people experience improved vision within a few hours. Over 90% of people achieve 20/20 vision and may no longer need glasses or contact lenses. There are potential side effects and risks, including dry eyes, temporary visual issues, and in rare cases, loss of vision.