Neurology is the specialty concerned with the nervous system. Your nervous system regulates and coordinates your body's activities. The central nervous system is consistent with the brain and spinal cord.
What is the nervous system?
The nervous system, made up of two major divisions, regulates and coordinates body activities. This complex system includes the following:
Central nervous system
Which consists of the brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral nervous system
Which consists of all other neural elements, including the peripheral nerves and the autonomic nerves. In addition to the brain and spinal cord, the principal organs of the nervous system include the following:
Eyes
Ears
Sensory organs of taste
Sensory organs of smell
Sensory receptors located in the skin, joints, muscles, and other parts of the body

What are the typical neurological diseases?
Stroke and cerebral hemorrhages
Multiple sclerosis
Parkinson’s disease
Impaired consciousness and memory disorders, dementia
Headaches and migraines
Vertigo
Sleep disorders
Diseases of the nerves and nerve roots, such as carpal tunnel syndrome and intervertebral disk problems
Polyneuropathy
Restless leg syndrome
Back pain
Signs & symptoms of nervous system disorders
Here we have a list of the most common signs of a nervous system disorder, although each person may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms include:
Persistent or sudden onset of a headache
A headache that changes or is different
Loss of feeling or tingling
Weakness or loss of muscle strength
Loss of sight or double vision
Memory loss
Impaired mental ability
Lack of coordination
Muscle rigidity
Tremors and seizures
Back pain which radiates to the feet, toes, or other parts of the body
Muscle wasting and slurred speech
New language impairment (expression or comprehension)
Although the symptoms of a nervous system disorder may look like other medical conditions. Make sure to see a professional for a diagnosis.
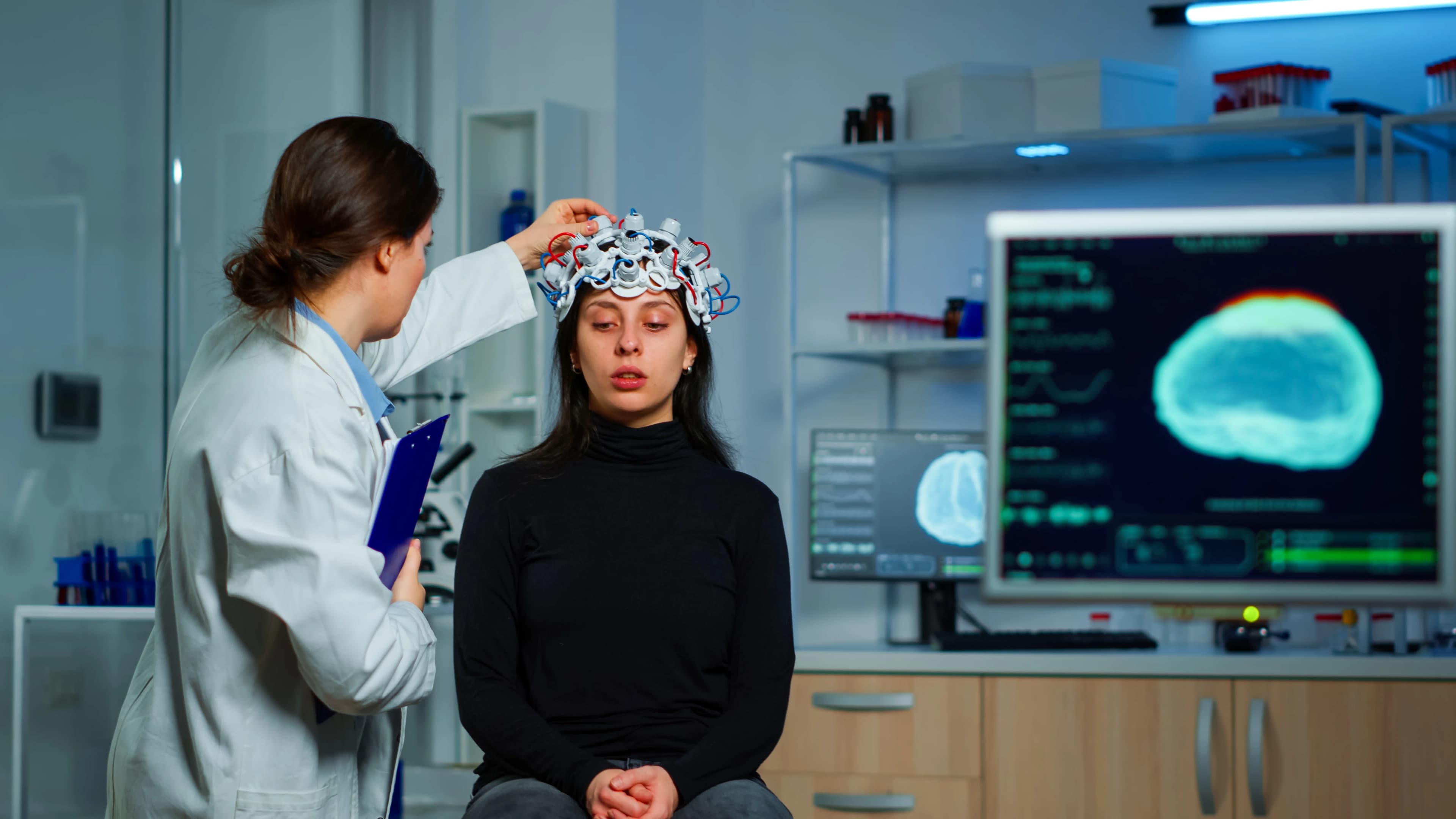
When should I see a neurologist?
You should keep in mind, that neurological disorders may present themselves in different parts of the body, for example, migraines, back pain, dizzy spells, changes in hearing and speech, and vision loss are all reasons to consult with a neurologist. Trembling, muscle stiffness, muscle weakness, and back pain radiating into the legs and arms should be examined. Some of the reasons to see a neurologist include:
Chronic or severe headaches: In case you’re experiencing migraine headaches, it’s probably necessary to make an appointment with your neurologist.
Chronic pain: If you are experiencing chronic pain, and your primary care doctor can’t help manage it, then you should get a referral to a neurologist since there could be another reason causing your symptoms.
Dizziness: Feeling like you’re spinning, or having difficulty keeping your balance could mean something more serious is happening.
Numbness or tingling: Numbness or tingling, especially when it occurs on one side of the body or comes on suddenly, could be a sign of a stroke or other serious condition.
Movement problems: Difficulty walking, shuffling your feet, tremors, and unintentional jerks, can all be signs of a nervous system problem.
Memory problems or confusion: Worsening memory problems, personality changes, or mixing up words could be signs of Alzheimer's disease.

What is the role of a neurologist?
During a full clinical neurological examination, the neurologist looks for external symptoms and tests nerve reflexes, paying attention to the person’s gait and posture to determine whether there is a disorder affecting the person’s ability to balance. Your body has 12 cranial nerves, which’s function can be impaired in brain disease, injury, or inflammation. Since each cranial nerve has a specific function, there are individual tests such as (smell, taste, vision, sound, and facial muscles…). During these examinations, usually, a person’s mental and psychological capacities are also tested. A memory test may also be performed if there appear to be any abnormalities.
Also based on the gathered results, additional diagnostics may be performed, including lab tests of blood and urine, or taking a sample of cerebrospinal fluid from the spinal canal (lumbar puncture).
NCV: Measuring nerve conduction velocity
EEG: Measuring brain waves (electroencephalography)
EMG: Measuring muscle activity (electromyography)
Evoked potentials: Every sensory stimulus in the body triggers brain activity that can be measured.
Doppler and duplex sonography: Ultrasound examinations of the vessels and brain
CT, MRI, PET: Additional brain imaging methods
Dementia testing
After carrying out the necessary examinations for the individual case, it is usually possible to diagnose one of the aforementioned neurological diseases as the cause.
Conclusion
Neurological disorders, encompassing a vast array of conditions affecting the nervous system, present some of the most complex challenges in modern medicine. The conclusion of any discussion on these disorders is not just a summary of symptoms and treatments, but a reflection on the human experience. These conditions can profoundly impact an individual's physical, cognitive, and emotional well-being, often altering the course of lives and the fabric of families. Yet, it is within this complexity that we find a relentless drive for understanding and innovation. As research advances, bringing new insights into genetics, neuroimaging, and pharmacology, our collective hope for preventing, managing, and curing these disorders grows stronger. The future holds promise for breakthroughs that will not only extend life expectancy but also improve the quality of life for those affected, reaffirming our commitment to overcoming some of humanity's most formidable health challenges.