An endocrinologist studies the body’s hormones. They can diagnose, treat, and manage several conditions affecting your endocrine system. Hormones are essential for our everyday survival. Your hormones control your temperature, sleep, mood, stress, growth, and more.
What is endocrinology?
Hormones are the chemical messengers that travel from one cell to another. Endocrinology is the study of every disease related to problems with hormones. Hormones are released in one part of the body, travel in the bloodstream, and have an effect on other parts of the body. Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands, such as the pituitary, thyroid, or adrenal glands. Hormones have a large role in many key bodily functions, such as:
Metabolism
Growth
Sexual function and reproduction
Sleep

Certain glands in your body called endocrine glands make and release hormones. Glands are special tissues in your body that create and release substances. The endocrine glands in your body include:
Adrenal glands
Parathyroid glands
Pineal gland
Pituitary gland
Any organism with more than one cell has hormones, which is why they are found in plants and animals. Your hormones influence or control physiological activities (growth, development, puberty, sugar regulation, and bone growth). Some of the major diseases of mankind such as diabetes, thyroid conditions, pituitary conditions, some sexual problems, some neurological problems, appetite and obesity, bone problems, cancer, etc. are influenced by hormones.
What are the different kinds of endocrinologists?
Diabetes and metabolism: Your hormones will play a part in how your body transforms the food you eat into energy metabolism. An endocrinologist can specialize in the treatment of different kinds of diabetes and other metabolic conditions such as obesity.
Thyroid disease: The butterfly-shaped gland in front of your neck, is your thyroid which can be affected by many conditions.
Endocrine oncology: Your endocrinologist could specialize in cancers that affect your endocrine system. Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer.
Neuroendocrinology: This branch of endocrinology studies the interaction between your nervous system and your endocrine system.
Pediatric endocrinology: Treating children who have endocrine conditions. Some endocrine conditions affect children specifically, and others can affect both children and adults.
Gender affirmation: Endocrinologists can specialize in sex hormone therapy, which is one aspect of gender affirmation.
Reproductive endocrinology: An endocrinologist could specialize in sexual function and fertility conditions. They may be referred to as fertility specialists.
Endocrinology nuclear medicine: This branch of endocrinology focuses on using nuclear medicine to treat certain endocrine conditions, especially thyroid conditions.
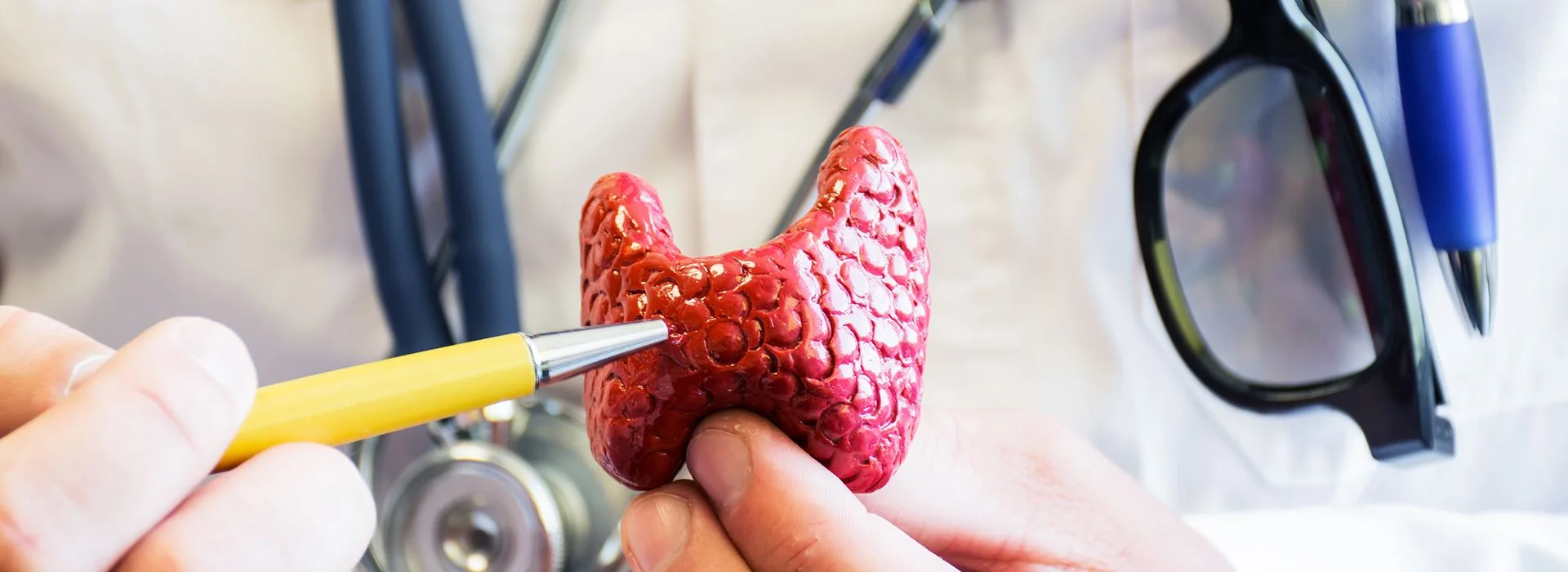
What does an endocrinologist treat?
Endocrinologists diagnose and treat conditions affecting the endocrine system. Conditions that endocrinologists treat can be categorized into these sections:
Diabetes and metabolic conditions
Endocrine cancers and tumors
Thyroid conditions
Metabolic conditions
Sexual development, function, and reproduction conditions
Calcium and bone conditions
Why should I see an endocrinologist?
Although a primary healthcare provider can diagnose and help you manage many endocrine conditions, you may benefit from seeing an endocrinologist since they’re likely more knowledgeable on your condition and more up-to-date on different medications, technology, and clinical trials that can help treat your condition. Endocrinologists are experts in endocrinology and endocrine conditions. If your primary healthcare provider suspects your body may be having issues with certain hormones, they may have you see an endocrinologist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Also, for treating conditions such as cancers and fertility issues, an endocrinologist could be part of the team.
What should I expect when seeing an endocrinologist?
You’ll most likely see an endocrinologist during an outpatient visit to their office. You can expect that they’ll ask thorough questions about your medical history, current medications, and symptoms. They may also perform a physical exam.
Conclusion
Endocrinology is a vital branch of medicine that focuses on the endocrine system, which comprises glands that produce and secrete hormones into the bloodstream. These hormones are chemical messengers that regulate a wide range of bodily processes, including metabolism, growth, development, and mood. Endocrine disorders, which can result from dysfunction in the peripheral endocrine gland itself or from issues with the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, can lead to hormone overproduction (hyperfunction) or underproduction (hypofunction). Conditions such as diabetes, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and various thyroid disorders fall under the purview of endocrinology. The field of endocrinology continues to evolve with advancements in diagnostic tools and treatment options, offering hope for improved management and treatment of endocrine disorders.
Read more: