Mammaplasty and mastectomy are two distinct surgical procedures often associated with breast health, but they serve different purposes and have different implications for patients.
Mammaplasty, also known as breast reduction or augmentation, is primarily a cosmetic procedure aimed at altering the size, shape, or appearance of the breasts. This surgery can be performed for various reasons, including alleviating physical discomfort caused by overly large breasts, improving self-esteem, or achieving a desired aesthetic. Reduction mammaplasty involves removing excess breast tissue, fat, and skin to achieve a breast size in proportion with the body, which can relieve symptoms like back, neck, and shoulder pain. On the other hand, augmentation mammaplasty involves the use of implants to increase breast size and improve shape. This procedure is often chosen by individuals seeking to enhance their physical appearance or restore breast volume lost after weight reduction or pregnancy.
Mastectomy, in contrast, is a surgical procedure primarily used to treat or prevent breast cancer. It involves the removal of one or both breasts, either partially or completely. There are different types of mastectomies, including total mastectomy, which removes the entire breast, and modified radical mastectomy, which also involves the removal of lymph nodes under the arm. Mastectomy is often recommended for patients with large or multiple areas of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) or invasive breast cancer. It can also be a preventive measure for those at high risk of developing breast cancer due to genetic factors.
While mammaplasty focuses on enhancing or reducing breast size for physical comfort or aesthetic reasons, mastectomy is a critical intervention for managing and preventing breast cancer. Both procedures can significantly impact a patient's quality of life, but they cater to different medical and personal needs. The choice between these surgeries depends on individual circumstances, including medical history, personal preferences, and overall health.
What is Mammaplasty?
Mammaplasty, also known as mammoplasty, refers to a group of surgical procedures designed to reshape or modify the appearance of the breasts. This term encompasses both augmentation and reduction surgeries, each serving different purposes and addressing various patient needs.
Augmentation mammaplasty: This is commonly performed to increase the size, change the shape, and/or alter the texture of the breasts. This procedure typically involves the surgical implantation of breast implants, which can be filled with either saline or silicone gel. The implants are placed either under the chest muscle or over it, depending on the patient's anatomy and desired outcome. Augmentation mammaplasty is often chosen by individuals seeking to enhance their physical appearance, restore breast volume lost after weight reduction or pregnancy, or achieve a more rounded breast shape. For some, this surgery is a way to boost self-confidence and improve body image.
Reduction mammaplasty: On the other hand, is performed to reduce the size of the breasts by removing excess breast tissue, fat, and skin. This procedure is often sought by individuals experiencing physical discomfort due to overly large breasts, such as chronic back, neck, and shoulder pain, skin irritation, and difficulty participating in physical activities. Reduction mammaplasty can significantly improve a patient's quality of life by alleviating these symptoms and making it easier to engage in daily activities. Additionally, it can enhance the overall proportion and appearance of the body, contributing to improved self-esteem.
Both types of mammaplasty involve careful planning and consideration. Patients typically undergo a thorough consultation with a board-certified plastic surgeon to discuss their goals, medical history, and any potential risks or complications. The surgeon will evaluate the patient's breast anatomy, skin quality, and overall health to determine the most appropriate surgical approach. Preoperative planning may include imaging studies, such as mammograms, to ensure the patient is a suitable candidate for surgery.
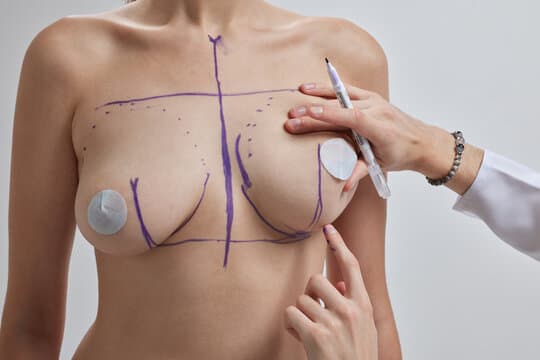
Pros & Cons of Mammaplasty
Mammaplasty, encompassing both breast augmentation and reduction, offers various benefits and drawbacks that individuals should consider before undergoing the procedure.
Pros of Mammaplasty
Enhanced Appearance and Self-Esteem: One of the primary advantages of mammaplasty is the improvement in breast appearance. Augmentation can enhance breast size and shape, while reduction can create a more proportionate figure. These changes often lead to increased self-confidence and a better body image.
Physical Comfort: For those undergoing reduction mammaplasty, the relief from physical discomfort is significant. Large breasts can cause chronic back, neck, and shoulder pain, skin irritation, and difficulty in physical activities. Reducing breast size can alleviate these issues, leading to a more active and comfortable lifestyle.
Clothing Fit: Both augmentation and reduction can improve the fit of clothing. Augmentation can help fill out clothing better, while reduction can make it easier to find well-fitting bras and clothes, enhancing overall comfort and style.
Symmetry Correction: Mammaplasty can address asymmetry in breast size and shape, providing a more balanced and aesthetically pleasing appearance.
Cons of Mammaplasty
Surgical Risks: As with any surgery, mammaplasty carries risks such as infection, bleeding, and adverse reactions to anesthesia. There is also the possibility of scarring, which can vary in severity depending on individual healing processes.
Recovery Time: The recovery period can be lengthy and uncomfortable. Patients may experience swelling, bruising, and pain, requiring time off work and limiting physical activities for several weeks.
Potential Complications: Complications such as implant rupture or capsular contracture (in augmentation) and changes in nipple sensation or breastfeeding difficulties (in reduction) can occur. These issues may necessitate additional surgeries to correct.
Cost: Mammaplasty can be expensive, and insurance may not cover cosmetic procedures. The financial burden includes not only the surgery itself but also potential follow-up treatments and revisions.
Unrealistic Expectations: It's crucial for patients to have realistic expectations about the outcomes. While mammaplasty can significantly improve appearance and comfort, it may not completely resolve all body image issues or physical discomforts.
What is Mastectomy?
Mastectomy is a surgical procedure involving the removal of one or both breasts, either partially or completely, primarily to treat or prevent breast cancer. This procedure is often recommended for patients with large or multiple areas of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) or invasive breast cancer, and for those at high risk of developing breast cancer due to genetic factors.
There are several types of mastectomies, each tailored to the patient's specific medical needs and cancer stage. A simple (or total) mastectomy involves the removal of the entire breast, including the nipple, areola, and most of the overlying skin. This type is often used when cancer is confined to the breast tissue.
A modified radical mastectomy combines a simple mastectomy with the removal of lymph nodes under the arm (axillary lymph node dissection), which helps in staging the cancer and determining the need for additional treatments.
A radical mastectomy, which is rarely performed today, involves the removal of the entire breast, the chest wall muscles under the breast, and all of the lymph nodes under the arm. This extensive surgery was once common but has largely been replaced by less invasive procedures that are equally effective. Skin-sparing mastectomy preserves most of the breast skin, removing only the breast tissue, nipple, and areola. This approach is often used in conjunction with immediate breast reconstruction, as it results in less scar tissue and a more natural-looking breast. Nipple-sparing mastectomy is similar but also preserves the nipple and areola, making it a suitable option for patients with small, early-stage cancers located away from the nipple.
The decision to undergo a mastectomy is complex and involves considering various factors, including the size and location of the tumor, the patient's medical history, genetic predisposition, and personal preferences. The procedure typically lasts between one to three hours and may require a hospital stay of a few days.
Pros & Cons of Mastectomy
A mastectomy, the surgical removal of one or both breasts, is a significant procedure often performed to treat or prevent breast cancer. It comes with various pros and cons that patients should consider carefully.
Pros of Mastectomy
Reduced Risk of Recurrence: One of the primary benefits of a mastectomy is the significant reduction in the risk of breast cancer recurrence. By removing the entire breast tissue, the likelihood of cancer returning in that area is minimized.
Peace of Mind: Many patients find peace of mind knowing that the primary site of cancer has been removed. This can alleviate anxiety related to the possibility of cancer recurrence.
Elimination of Radiation Therapy: In many cases, a mastectomy can eliminate the need for radiation therapy, which is often required after a lumpectomy (breast-conserving surgery). This can reduce the overall treatment burden and associated side effects.
Prophylactic Option: For individuals with a high genetic risk of breast cancer (e.g., BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations), a prophylactic mastectomy can significantly reduce the risk of developing breast cancer in the future.
Cons of Mastectomy
Surgical Risks: As with any major surgery, mastectomy carries risks such as infection, bleeding, and complications from anesthesia. Additionally, there can be significant post-operative pain and a lengthy recovery period.
Loss of Sensation: Mastectomy often results in the loss of sensation in the chest area, which can affect a person's body image and sexual health. This loss of sensation is usually permanent.
Emotional and Psychological Impact: The removal of one or both breasts can have a profound emotional and psychological impact. Many patients experience feelings of loss, grief, and changes in self-identity. Counseling and support groups can be beneficial in coping with these changes.
Reconstructive Surgery: While reconstructive surgery is an option for many patients, it involves additional procedures, recovery time, and potential complications. Not all patients are candidates for reconstruction, and some may choose not to undergo further surgery.
Cost and Accessibility: The cost of mastectomy and subsequent reconstructive surgery can be high, and not all insurance plans cover these procedures fully. Accessibility to skilled surgeons and comprehensive care can also vary depending on geographic location and healthcare systems.
Differences between Mammaplasty & Mastectomy: Methods & Procedure
Mammaplasty and mastectomy are two distinct surgical procedures involving the breasts, each with different goals, methods, and implications. While both mammaplasty and mastectomy involve surgical procedures on the breasts, their purposes, methods, and implications differ significantly. Mammaplasty focuses on cosmetic enhancement or reduction for comfort and aesthetic reasons, whereas mastectomy is a critical procedure for the treatment or prevention of breast cancer. Understanding these differences is crucial for patients making informed decisions about their surgical options.
The methods and procedures for mastectomy are more extensive and invasive compared to mammaplasty. Mastectomy often requires a longer recovery period and may involve additional treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Post-mastectomy, patients may opt for breast reconstruction, which can be done using implants or autologous tissue (tissue from another part of the patient's body). This reconstruction can be performed immediately following the mastectomy or at a later date.
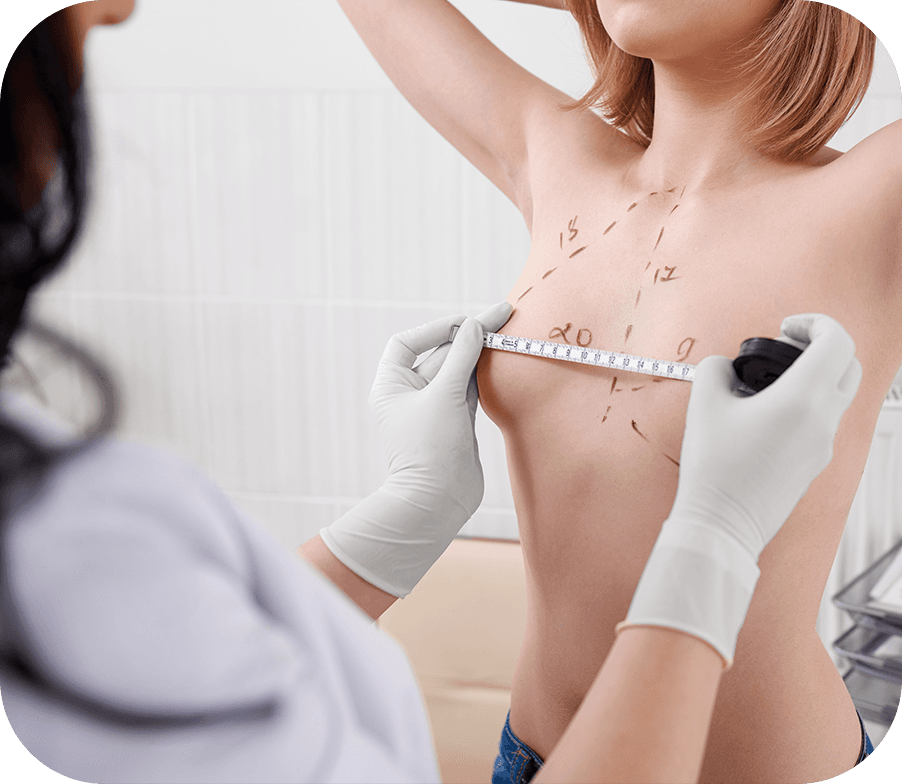
Mammaplasty, also known as breast augmentation or reduction, is primarily performed for cosmetic or reconstructive purposes. There are two main types: augmentation mammaplasty and reduction mammaplasty. Augmentation mammaplasty typically involves making incisions in inconspicuous areas to minimize visible scarring, such as under the breast, around the areola, or in the armpit. The implants are then placed either under the breast tissue or beneath the chest muscle. Reduction mammaplasty, on the other hand, is performed to remove excess breast tissue, fat, and skin to alleviate discomfort caused by overly large breasts. The surgery involves making incisions around the areola and down to the breast crease, removing the excess tissue, and reshaping the remaining breast tissue.
Mastectomy, in contrast, is a surgical procedure primarily used to treat or prevent breast cancer. It involves the removal of one or both breasts, either partially or completely. There are several types of mastectomy, including total (simple) mastectomy, which removes the entire breast; modified radical mastectomy, which removes the entire breast along with some of the lymph nodes under the arm; and radical mastectomy, which removes the breast, chest muscles, and all of the lymph nodes under the arm.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while both mammaplasty and mastectomy involve surgical procedures on the breasts, they serve fundamentally different purposes and have distinct methods and implications. Mammaplasty, encompassing both augmentation and reduction, primarily aims to enhance or reduce breast size for cosmetic or comfort reasons, significantly impacting a person's self-image and quality of life. In contrast, mastectomy is a critical procedure for the treatment or prevention of breast cancer, involving the removal of breast tissue to reduce the risk of cancer recurrence. The choice between these procedures depends on individual needs, medical conditions, and personal preferences.
Read More