Choosing the best material for knee replacement is a crucial decision that can significantly impact the success and longevity of the implant. The most commonly used materials include metal-on-plastic, ceramic-on-ceramic, and metal-on-metal combinations.
Knee Replacement Material
Knee replacement materials are critical components in ensuring the success and longevity of knee implants. The primary materials used in knee replacement surgeries include metal alloys, ceramics, and polyethylene plastics. Metal-on-plastic implants, which consist of a metal femoral component and a polyethylene plastic spacer, are the most commonly used due to their durability and long track record. These materials help provide smooth articulation and reduce friction within the joint. Ceramic-on-ceramic implants, featuring ceramic components for both the femoral and tibial parts, offer excellent biocompatibility and resistance to wear, making them a suitable option for those with metal sensitivities. However, they can sometimes produce a squeaking noise. Metal-on-metal implants, while less common today due to concerns about metal ion release and potential complications, were previously favored for their durability and ability to withstand high levels of activity. Choosing the best material for a knee replacement often depends on individual factors such as the patient's activity level, age, weight, and any specific allergies or sensitivities. Consulting with an experienced orthopedic surgeon is essential to determine the most appropriate material for a successful and long-lasting knee replacement.
Types of knee replacement materials
Knee replacement materials play a crucial role in the success and longevity of knee implants, with several types designed to cater to different patient needs and preferences. The most commonly used materials in knee replacement surgeries are metal alloys, ceramics, and polyethylene plastics, each offering distinct advantages. Choosing the best knee replacement material involves considering the patient's age, activity level, weight, and any allergies or sensitivities.
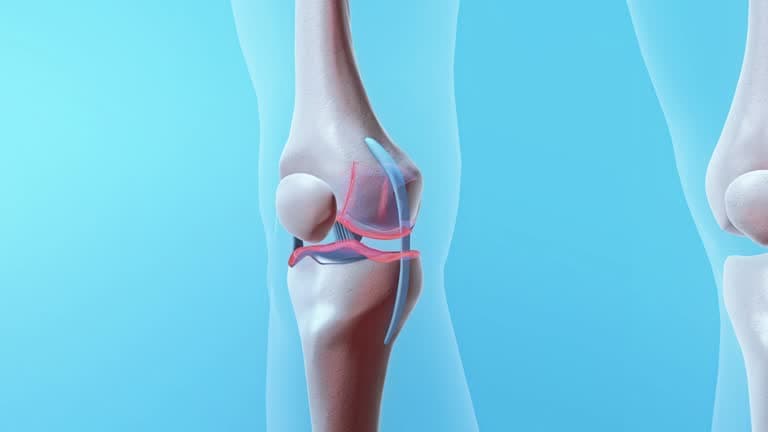
Metal implants
Knee replacement metal implants are a crucial component in modern orthopedic surgery, designed to restore function and alleviate pain in patients with severe knee damage or arthritis. These implants are typically made from durable metal alloys, such as cobalt-chromium or titanium, which are selected for their strength, biocompatibility, and resistance to wear. The primary structure of a knee implant consists of a metal femoral component that fits over the end of the thigh bone (femur) and a metal tibial component that covers the top of the shinbone (tibia). Between these metal parts, a polyethylene (plastic) insert acts as a smooth, low-friction surface, mimicking the natural cartilage in a healthy knee.
The metal femoral component is contoured to replicate the natural shape of the end of the femur, allowing for a range of motion similar to that of a natural knee. The tibial component includes a flat metal plate that sits on top of the tibia, providing stability and support to the implant. This combination of metal and plastic helps ensure the artificial joint can withstand the significant forces and movements experienced during daily activities, such as walking, climbing stairs, and even running.
One of the main advantages of metal implants is their longevity. With advancements in materials and design, modern metal implants can last 15 to 20 years or more, significantly improving the quality of life for patients. Additionally, the biocompatibility of metal alloys used in knee implants minimizes the risk of adverse reactions and promotes successful integration with the surrounding bone.
Patients considering knee replacement surgery should discuss the specific type of metal implant with their orthopedic surgeon, as individual factors such as age, activity level, and any potential allergies or sensitivities need to be considered. The surgeon's expertise and the patient's unique circumstances will guide the selection of the most appropriate implant material, ensuring a successful and long-lasting knee replacement outcome.
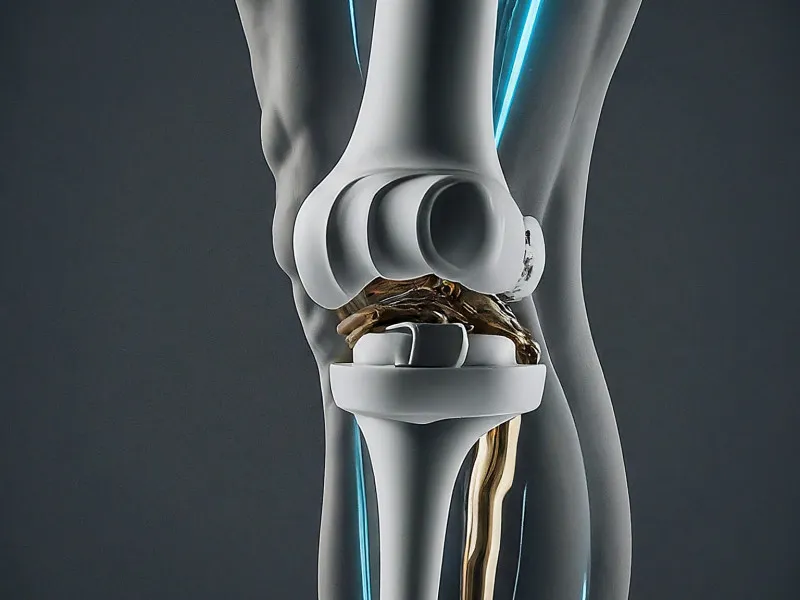
Plastic implants
Knee replacement plastic implants play a crucial role in modern orthopedic surgeries, providing a smooth and durable surface that mimics the natural cartilage in a healthy knee. These implants are typically made from high-density polyethylene, a type of medical-grade plastic known for its excellent wear resistance and biocompatibility. In a knee replacement procedure, the plastic component, often referred to as the polyethylene insert or spacer, is positioned between the metal femoral and tibial components. This insert acts as a cushion, facilitating smooth movement and reducing friction between the metal parts of the implant.
The polyethylene insert is designed to withstand the significant stresses and movements encountered during daily activities, such as walking, climbing stairs, and even running. Its durability ensures that the knee joint can function effectively for many years, often lasting 15 to 20 years or more, depending on the patient's activity level and adherence to post-operative care. The plastic material is also less likely to cause allergic reactions compared to metal, making it a suitable option for patients with metal sensitivities.
One of the key advantages of using polyethylene in knee implants is its ability to distribute load evenly across the joint, reducing the risk of implant loosening and wear over time. Advances in manufacturing techniques have further improved the quality and longevity of polyethylene inserts, making them an integral part of modern knee replacement systems. These improvements include cross-linking the polyethylene molecules, which enhances the material's strength and wear resistance.
Patients considering knee replacement surgery should discuss the specific type of plastic implant with their orthopedic surgeon, as the choice of materials can impact the overall success and longevity of the procedure. The surgeon's expertise, combined with the patient's unique circumstances, will guide the selection of the most appropriate implant, ensuring a successful and durable knee replacement outcome. Proper care and regular follow-up appointments are essential to maintain the functionality and longevity of the plastic implant, contributing to an improved quality of life for patients.
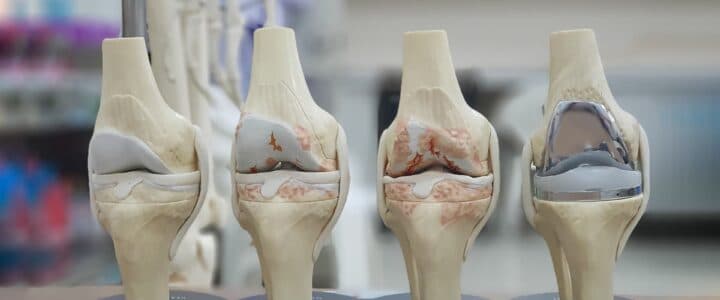
Ceramic implants
Knee replacement ceramic implants are a sophisticated option in orthopedic surgery, designed to enhance the durability and performance of knee prostheses. These implants utilize ceramic materials, renowned for their exceptional biocompatibility and resistance to wear. The use of ceramics in knee replacements aims to provide a longer-lasting and more stable joint, particularly beneficial for patients with metal sensitivities or allergies. Ceramic-on-ceramic knee implants consist of a ceramic femoral component and a ceramic tibial component, offering a highly smooth surface that reduces friction and wear. This configuration minimizes the production of wear particles, which can cause inflammation and complications in other types of implants.
One of the significant advantages of ceramic implants is their excellent wear resistance. Ceramic materials are incredibly hard and durable, allowing them to withstand the constant stress and movement experienced by knee joints. This property makes ceramic implants an attractive choice for younger, more active patients who require a longer-lasting solution. Additionally, ceramics are biologically inert, meaning they do not react with body tissues, reducing the risk of adverse reactions and improving overall patient outcomes.
However, there are some considerations with ceramic implants. They can be more brittle than metal, posing a higher risk of fracture under extreme conditions. This brittleness necessitates careful consideration by the orthopedic surgeon when recommending ceramic implants, particularly for patients with high-impact activities. Despite this, advancements in ceramic technology have led to the development of stronger, more fracture-resistant materials, expanding their applicability and reliability.
Patients considering knee replacement surgery should consult with their orthopedic surgeon to discuss the potential benefits and risks of ceramic implants. The surgeon will evaluate factors such as the patient's age, activity level, and overall health to determine the most suitable implant material. With proper selection and surgical expertise, ceramic knee implants can offer a durable, long-lasting solution that enhances the quality of life for patients undergoing knee replacement surgery.
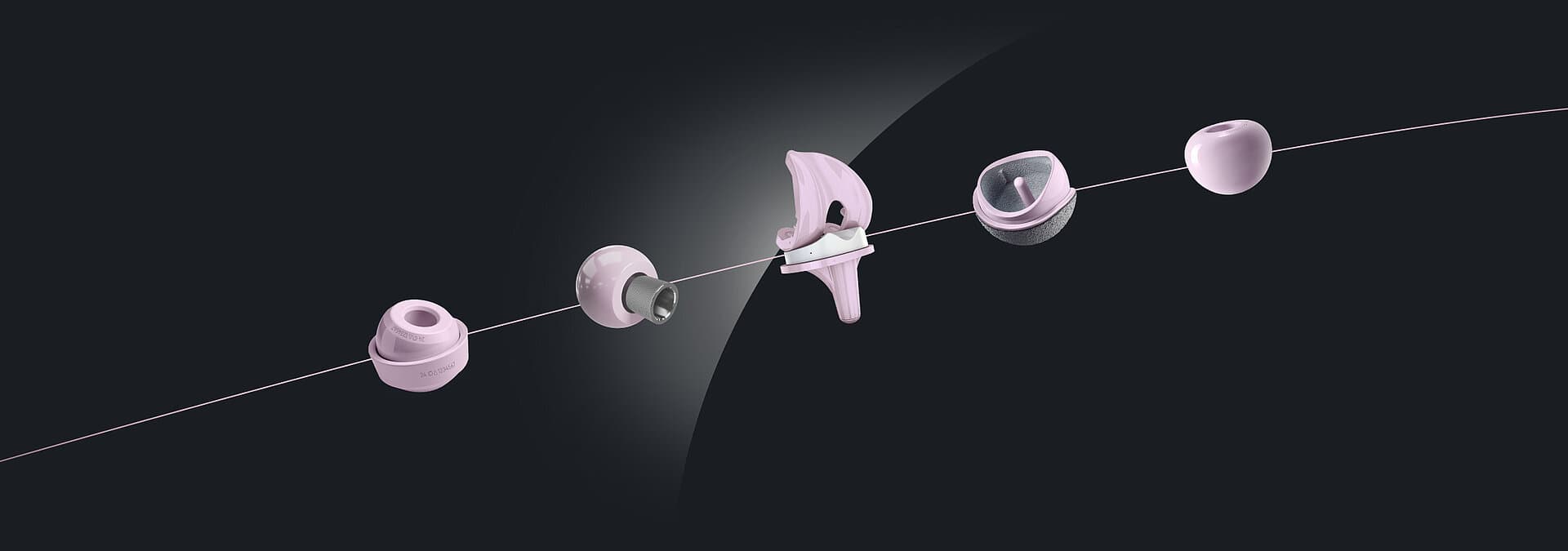
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice of knee replacement materials is a critical factor in the success and longevity of the implant. Metal-on-plastic implants are widely favored for their durability and proven track record, offering a reliable option for many patients. Ceramic-on-ceramic implants provide excellent biocompatibility and wear resistance, making them suitable for individuals with metal sensitivities. While less common, metal-on-metal implants can still be considered for younger, more active patients, although their use has declined due to concerns about metal ion release. Ultimately, the best material for a knee replacement depends on individual factors such as age, activity level, overall health, and specific needs.
Read More